Data security and data privacy are different concepts that people often get mixed up. Some mistakenly use them interchangeably. However, they're not the same thing.
Data security protects information from unauthorized access, use, and disclosure. It also protects it from disruption, modification, or destruction. Data privacy is the right to control who gets to see your personal information like credit card numbers and bank account balances.
Data security focuses on protecting data, whereas data privacy is about controlling what others can do with the information after they have accessed it.
Private data and security should be taken seriously by individuals and organizations that manage or collect data. Both are essential concerns in protecting sensitive information like identities, finances, or health records.
With that said, the difference between data security vs. data privacy can be confusing for some people, so we're going to break down their similarities and differences in this article, as well as potential legal implications for your business.
Our Privacy Policy Generator makes it easy to create a Privacy Policy for your business. Just follow these steps:
-
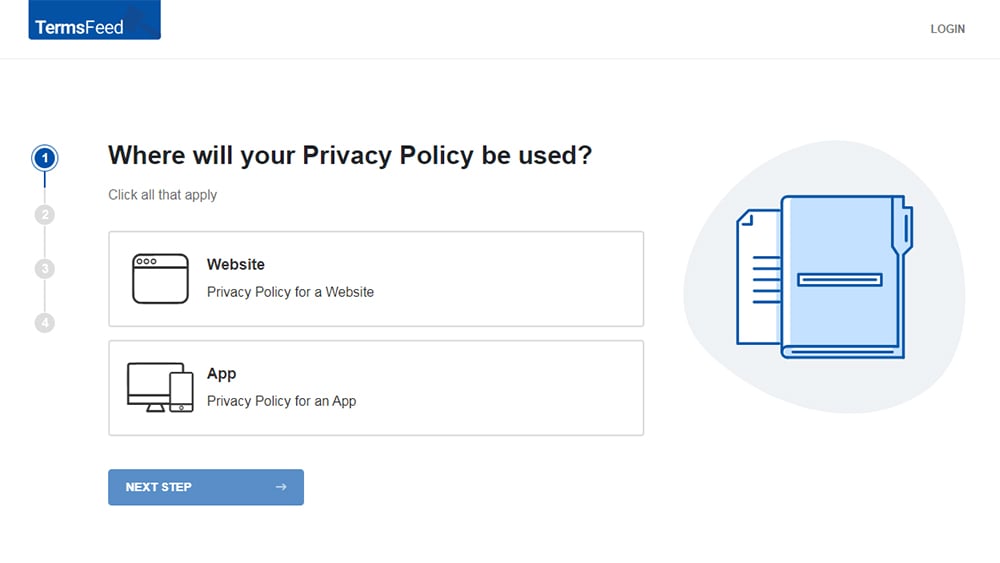
At Step 1, select the Website option or App option or both.
-
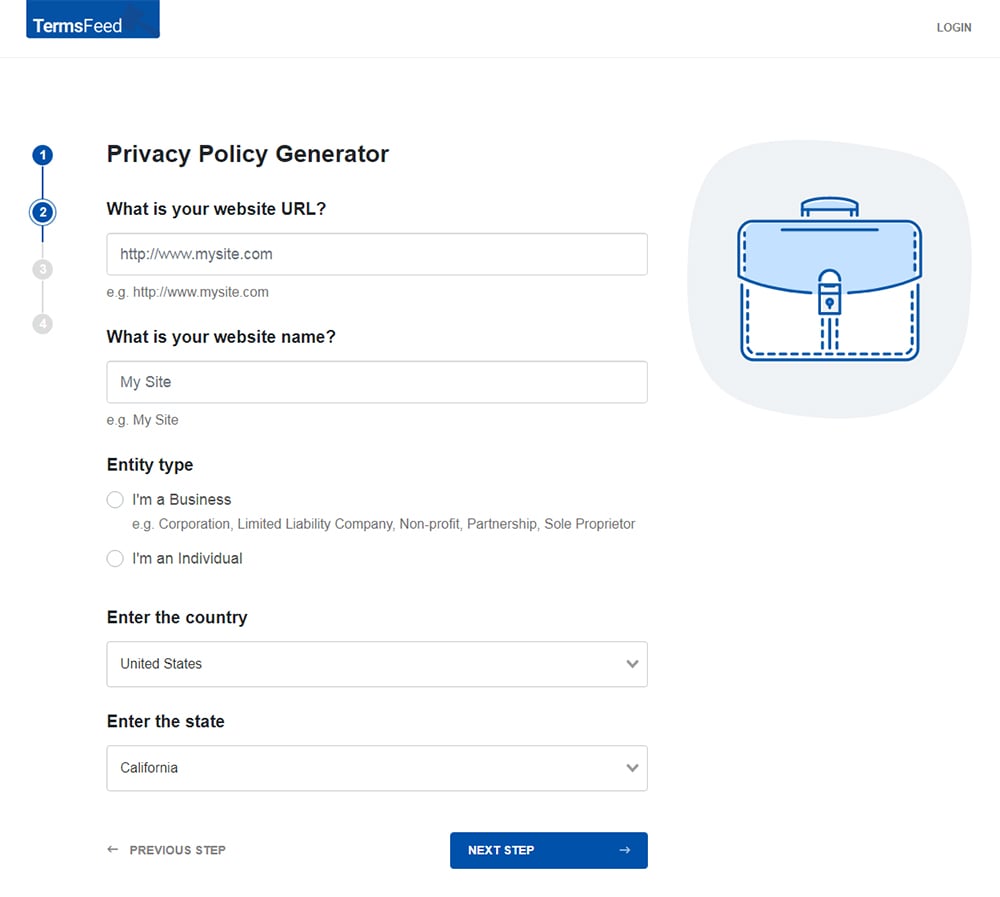
Answer some questions about your website or app.
-
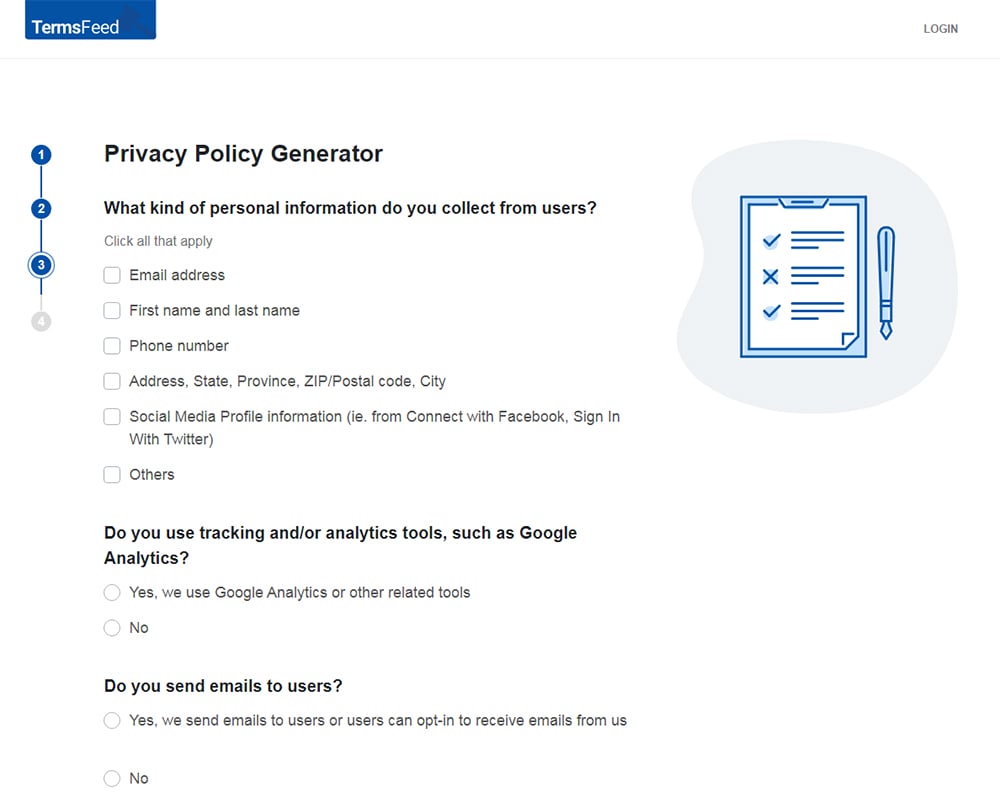
Answer some questions about your business.
-
Enter the email address where you'd like the Privacy Policy delivered and click "Generate."
You'll be able to instantly access and download your new Privacy Policy.
- 1. Why is it Important to Understand the Differences?
- 1.1. You Risk a Data Breach Without Proper Security
- 1.2. You Could Be Violating Various Privacy Regulations
- 2. What is Data Security?
- 3. What is Data Privacy?
- 3.1. Data Privacy and U.S. Law
- 3.2. Data Privacy and the GDPR
- 4. Similarities and Differences Between Data Security and Data Privacy
- 5. Best Practices for Ensuring Data Security
- 6. Best Practices for Ensuring Adequate Data Privacy
- 7. Summary
Why is it Important to Understand the Differences?
It is crucial that your company understands and addresses the consequences of all the laws in place to protect consumer privacy and data.
Data security and data privacy are essential for businesses because they help lessen the impact of data breaches, theft of information, and other misuse of data. Data is a large part of today's digital world, so it becomes necessary to protect this information as much as possible. This is where data security vs. data privacy comes in (and why we're writing an article about them).
Data privacy laws aren't all the same and they differ from country to country, but most have some sort of regulation that requires protection against unauthorized access and disclosure of personal information.
If these policies aren't upheld, your business could face fines & lawsuits that can be financially detrimental. Not only will you lose customers if there's a breach, but you could also incur legal fees if sued by those affected.
It is your responsibility as the owner of a business to protect the data in your possession. This includes protecting the data and privacy of your customers, employees, partners, customers, and all other contacts.
Many unpleasant scenarios could occur if you don't have the proper measures in place.
You Risk a Data Breach Without Proper Security
If you don't have security measures implemented, such as multi-device management, multi-factor authentication, or identity management, your business could be at risk for a breach.
Your data is your most valuable asset, other than employees. A breach can be a colossal threat to your company and could even cause it to go out of business.
For example, about 60% of hacked small and medium-sized businesses go out of business after six months.
You Could Be Violating Various Privacy Regulations
You could be violating a number of regulations if you don't have the suitable measures in place for keeping your customer or employee data private. For example, healthcare companies must adhere to HIPPA and not share patient information. This personal data should not be sold or distributed without consent.
You could end up violating the law as well as creating disgruntled customers that will eventually leave you in favor of a more conscientious competitor. It can have a massive impact on your revenue, both in terms of fines and losing customers. You could also damage your reputation.
With the information above in mind, let's take a look at what data security and privacy actually are.
What is Data Security?

Data security is the protection of information. You must protect data with high value or sensitivity against hackers, competitors, and other unauthorized parties.
For example, IBM's definition reads like this:
"Data security is the practice of protecting digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, or theft throughout its entire lifecycle."
Properly implemented data security strategies can protect your organization's information assets from cybercriminals. They also protect against insider threats and human error, which are the leading causes of data breaches today.
Tools used to protect data include the following:
- Encryption
- Data masking and redaction
- Automated reporting to simplify audits and comply with regulatory requirements
- Protect data according to its level of importance by assigning it a classification consisting of four categories: public, internal use, sensitive; and top-secret
Additionally, data security entails using sophisticated hardware systems and secure facilities designed to preserve the integrity of the data, which means that it is accurate, reliable and that authorized parties have access to it.
Data security methods and processes may also include:
- Activity monitoring
- Network security
- Access control
- Breach response
- Multi-factor authentication
What is Data Privacy?

There are various privacy definitions online, but data privacy is generally concerned with the correct way to handle, process, store, and use personal information. It is all about individual rights with respect to their personal information.
Data privacy is often confused with terms like security, confidentiality, or anonymity, which overlap but are different concepts.
Data privacy can also refer to control over what details about oneself are made available, by whom, and when.
Some of the most common issues raised by privacy advocates include:
- Managing contracts or policies
- Applying governing regulation or law like Europe' General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or California's Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) as amended by the CPRA
- Third-party management of personal data
In general, privacy is an individual's right to freedom from the intrusion of others into personal areas of life and to have others leave them alone.
Privacy is guaranteed by many countries' constitutions, making it a fundamental human right. The idea is universally accepted and is one of the core principles that define human dignity.
Any risk assessment conducted to enhance the privacy of individuals' personal data is performed to protect the rights and freedoms of those individuals.
Data Privacy and U.S. Law

Data privacy is the element of information technology (IT) that deals with the ability of an individual or organization to determine what data in a computer system can be shared with third parties.
The United States has a sectoral approach to data privacy legislation. This means that every law or compliance regulation relating to data privacy was created according to the needs of one particular industry or segment of the population.
Examples include:
Children's Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) - Gives parents control over what information websites can collect from their kids.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) - Ensures patient confidentiality for all healthcare-related data.
Electronic Communications Privacy Act (ECPA) - Extends government restrictions on wiretaps to include transmissions of electronic data.
Video Privacy Protection Act - Prevents wrongful disclosure of an individual's personally identifiable information stemming from their rental or purchase of audiovisual material.
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act - Mandates how financial institutions must deal with the private information of individuals.
Data Privacy and the GDPR

There are two main categories of compliance that organizations must understand in order to comply with the GDPR: Data privacy and data protection.
Chapter 3 of the GDPR lays out the data privacy rights and principles that all "natural persons" are guaranteed under EU law. These rights are your responsibility as an organization. You could face penalties if you fail to live up to your obligations under the law.
As a business, you have to explain how you process data in "a concise, transparent, intelligible and easily accessible form, using clear and plain language."
People must be able to contact you easily (e.g., to request erasure, etc.). You must respond quickly to these requests and provide adequate information.
Discussing all of the GDPR requirements for data privacy is beyond the scope of this article, but essentially you must make every effort to provide people with the tools and means to limit who can access their data.
Transparency and open communication are vital in allowing people to know how their data is used and collected. You must make it easy for customers and users to exercise their rights (of access, erasure, etc.).
Similarities and Differences Between Data Security and Data Privacy

By now, it should be clear that data security and data privacy are not the same things. Data privacy concerns the proper use, collection, retention, and deletion of data, while data security covers policies, methods, and the means to protect personal data.
For instance, if you use a secure email service like a ProtonMail account, then your password is a data security method. However, the way ProtonMail uses your data for account administration would be considered a data privacy issue.
Keep in mind that data security is a precondition for data privacy. And information security is the main requirement to ensure data privacy.
Data security can exist without data privacy, but not vice versa.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Security

There are many options available for data storage and management, which can help ensure data security. Some of them, like encrypting data we mentioned previously, include the following:
- Engage in data loss prevention (DLP), a collection of strategies and tools to help prevent data from being lost, stolen, or accidentally deleted. Many data loss prevention strategies include multiple tools that protect against and recover data loss.
- Use storage with built-in data protection. Modern storage equipment provides built-in disk clustering and redundancy.
- Use firewalls, which are utilities that will enable you to filter and monitor network traffic. Firewalls may be used to restrict access to data and to prevent unauthorized users from transferring it.
- Use authentication and authorization controls that help you verify credentials and assure that user privileges are applied correctly. These measures can be used in conjunction with role-based access control (RBAC) and as part of identity management (IAM) or any other solution that helps you manage access to your data.
- Use endpoint protection, which protects your network's gateways. This includes ports, routers, and connected devices. Endpoint protection software allows you to monitor and filter traffic around your network.
- Erase your data. This reduces liability by deleting data no longer required. This can be done when data has been processed and analyzed or whenever data becomes irrelevant.
Best Practices for Ensuring Adequate Data Privacy

A relatively recent survey found that 63% of Americans would not consent to sharing their personal data to receive ads for a free service. This is due to a recent increase in public awareness about privacy and its impact on people. Much of this is thanks to the high-profile demands of GDPR and CCPA (CPRA) compliance.
Privacy is now a significant concern for everyone. The public at large has a better understanding of privacy than ever before. Because of this, data privacy now touches both your company and your customers.
Best practices you should therefore employ include:
- Practicing minimal data collection - Make sure that you have the right policies in place to ensure that only necessary data are collected. You can increase your risk and put your security team under unnecessary strain if you collect more data than you actually need. Data minimization can help you reduce bandwidth and storage costs.
- Involve your users - Privacy concerns are well-known to many users, and they are likely to be open to receiving transparency about how your data is used and stored. The GDPR makes consent an integral part of data collection and use. By incorporating privacy concerns into your interfaces, you can ensure that users are included and consent to your processes.
- Take stock of your data - Data privacy can be achieved by understanding the data you possess, how it is used, and where it is stored. You should outline how you collect and use this information in your policies.
Summary
In conclusion, data security and data privacy are two different concepts with various areas of overlap.
Data security is about protecting the availability and integrity of data, while data privacy concerns your data's confidentiality and use.
Data security covers policies, methods, and the means to protect personal data, while data privacy deals with how that protected data is used.
It's essential to understand both concepts and their differences because you'll be expected to implement policies within your company that address them. Data protection and privacy laws are increasing globally and in the level of strictness with which businesses are expected to comply.
As a business owner, you should employ best practices for both data security and privacy to ensure compliance with major legislation like the GDPR and the CCPA (CPRA).

Comprehensive compliance starts with a Privacy Policy.
Comply with the law with our agreements, policies, and consent banners. Everything is included.