Online businesses use website tracking to personalize their content and services for clients who might be interested in them. However, this isn't always favored by the people being tracked.
Some online users take issue with people/companies collecting their data to use without their consent. Online businesses that collect this data to personalize their content and services for clients who might be interested in them will need to do so in a legal way.
This article will explain what website tracking is, how to do it, and the laws and policies that guide the process.
Our Privacy Policy Generator makes it easy to create a Privacy Policy for your business. Just follow these steps:
-
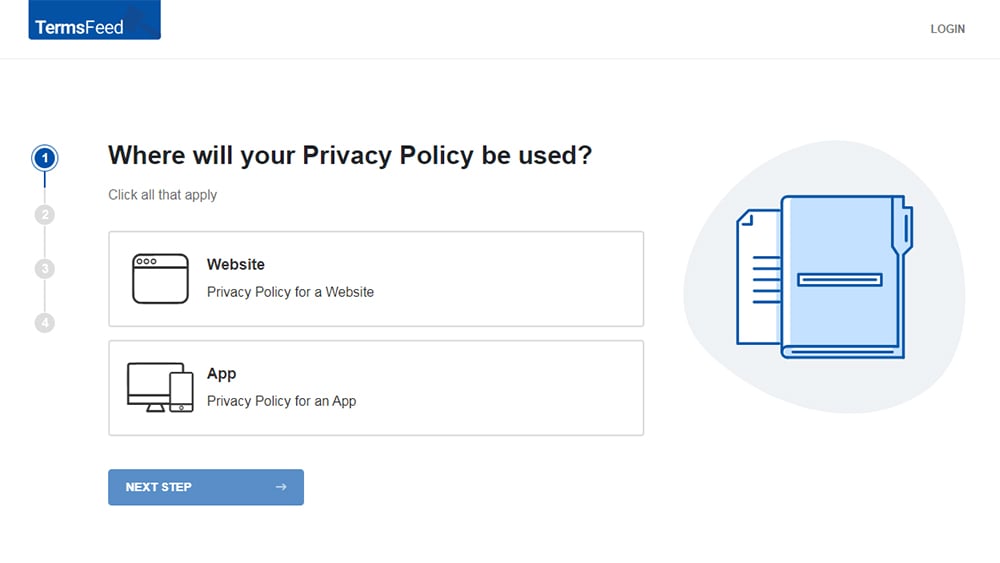
At Step 1, select the Website option or App option or both.
-
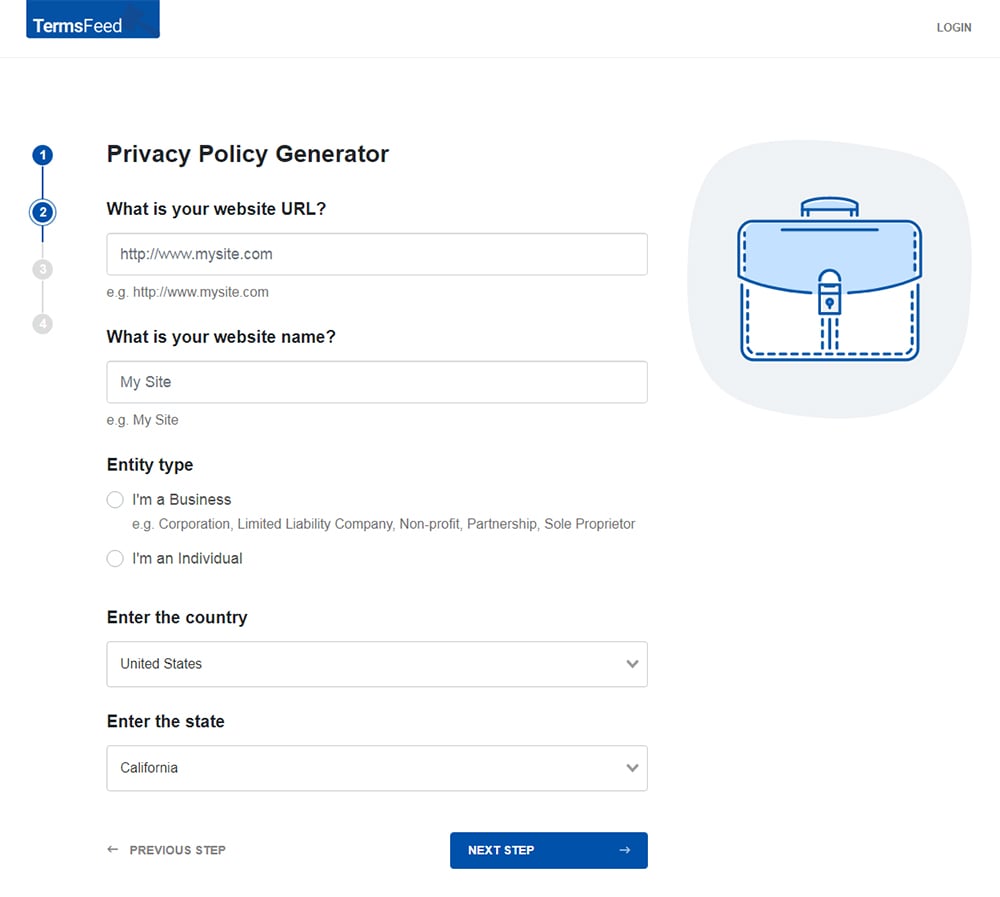
Answer some questions about your website or app.
-
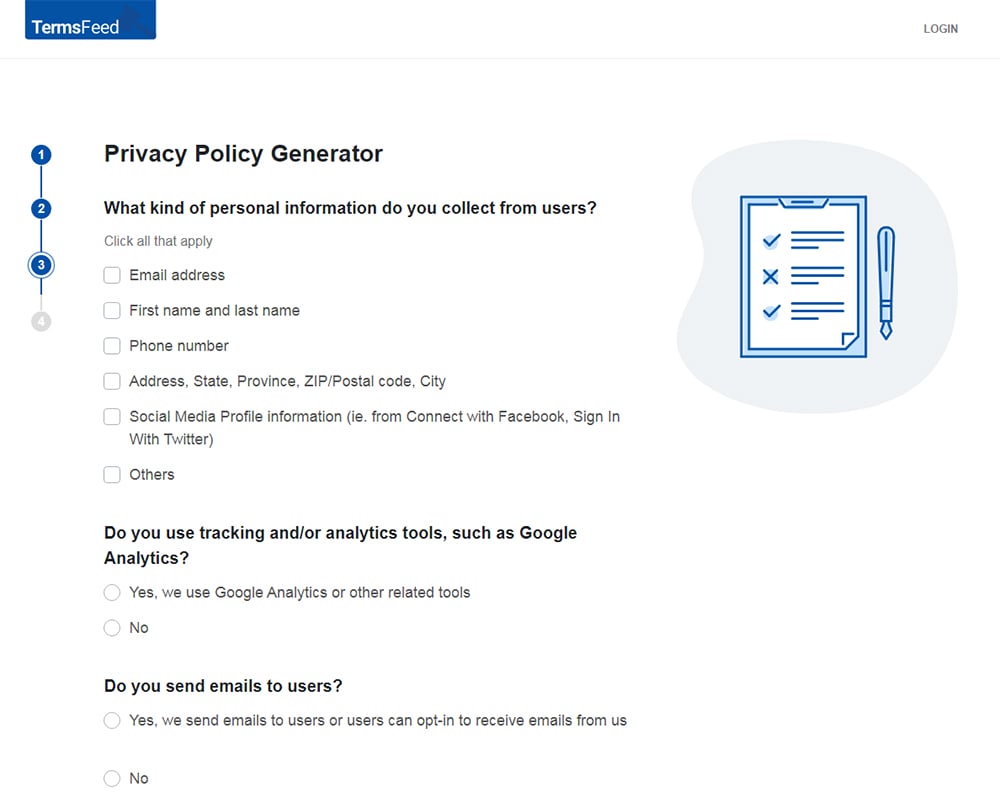
Answer some questions about your business.
-
Enter the email address where you'd like the Privacy Policy delivered and click "Generate."
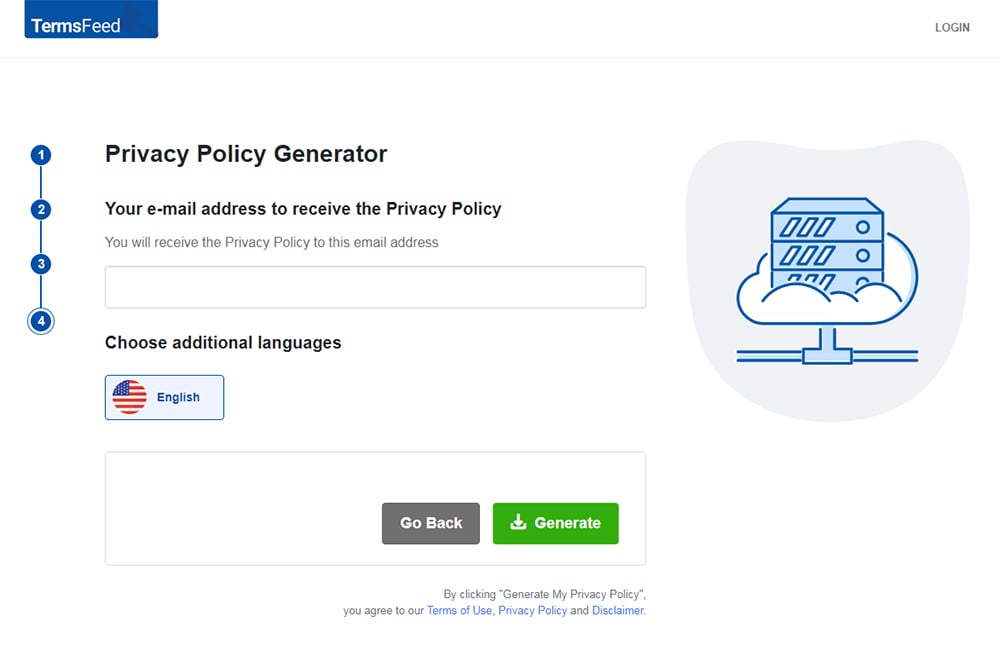
You'll be able to instantly access and download your new Privacy Policy.
- 1. What is Website Tracking?
- 2. How Do Websites Track User Data?
- 2.1. IP Tracking
- 2.2. Cookies
- 2.3. Pixel Tracking
- 2.4. Fingerprinting
- 2.5. Device Tracking
- 3. What are Some Popular Website Tracking Methods?
- 4. What are Some Perks of Website Tracking?
- 4.1. How Do Users Benefit From Website Tracking?
- 4.2. How Do Businesses Benefit From Website Tracking?
- 5. Is it Legal to Engage in Website Tracking?
- 6. What Laws Regulate Website Tracking?
- 6.1. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- 6.2. California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
- 6.3. Website Tracking Policies in Brazil and South Africa
- 7. How Do You Compliantly Engage in Website Tracking?
- 7.1. Adopt and Implement Privacy-First Tracking Practices
- 7.2. Always Obtain Valid Legal Consent
- 7.3. Store Detailed Consent Records
- 7.4. Use a Consent Management Platform
- 8. Summary
What is Website Tracking?
Website tracking (also called web tracking) is a method of using cookies and other tracking technologies to track and analyze user data anonymously.
These cookies and tracking technologies typically harvest the following information from users:
- Names
- Email addresses
- IP addresses
- Geographical locations
- Browser and search histories
- Purchase history and credit card information
- Shopping and purchase histories
- Product preferences
- Sexual orientation, political and social affiliations
How Do Websites Track User Data?
Before going any further, you should understand two main types of user tracking: first-party and third-party.
First-party tracking applies where only the domain a user visits collects their data. In contrast, third-party tracking involves a different party accessing user data apart from the domain they are on.
Here are the different technologies used by websites to track user data.
IP Tracking
Since every device connected to the internet uses a specific Identification Protocol (IP) address, analytics tools use the geographical location associated with the IP address to approximate user location.
This helps the business understand where most of its users are located to segment their market and target specific audiences based on where they are from.
Cookies
Cookies are text files installed by web analytics to identify users on their websites and track them when they visit other sites.
Here are the different types of cookies and what they do:
- First-party cookies are generated by the website a user visits and are only active for operations on that website.
- Third-party cookies, such as advertisement cookies, are used by third-party sites that track users' activities in multiple domains until deleted.
- Session cookies are one-session cookies that temporarily store user data until the session times out.
- Persistent cookies are permanent cookies that store user data until permanently deleted by the user.
Pixel Tracking
Pixels are tiny images that form the images we see on our screens. Tracking pixels are placed in HTML web pages to alert the analytics tool of visitors on the page.
Fingerprinting
This process identifies a unique identifier from the user's browser and computer settings, which tracks the user's browsing activity across multiple web pages.
The unique fingerprint can be:
- The device OS
- Screen resolution
- Fonts
- The browser version
- Browser extensions or add-ons
Device Tracking
Many analytics tools collect and analyze user devices and their specs (type of OS or browser), but this mainly applies when troubleshooting bugs and other design issues on specific devices or browsers.
Website tracking helps companies understand user preferences by knowing what their visitors search for on their browsers or the pages they like or follow on social media.
What are Some Popular Website Tracking Methods?
Businesses employ different website tracking techniques depending on the kind of data needed and its purpose thereafter. The most popular web tracking methods include the following.
- Advertising tracking: Checks the performance of ads on websites and social media, for example, Facebook ads and sponsored Instagram posts
- Preference tracking: Analyzes individual behavior, such as users' shopping habits and what makes them unique from other users.
- UX tracking: Details a user's online behavior and helps improve their online experience. It includes bug detection and interface design.
- Traffic tracking: Measures the website traffic, e.g., analytics, and helps the business gauge its online success and reach.
What are Some Perks of Website Tracking?
Website tracking comes with perks and benefits to both the internet user and the online business if applied progressively. Some of the perks are outlined next.
How Do Users Benefit From Website Tracking?
Some perks of website tracking are instrumental in an internet user's daily online activities. They include:
- Website tracking (temporarily) remembers users' login credentials when they abruptly leave the web page, so they continue filling shopping carts on Amazon or eBay upon return.
- Once businesses know what their clients like, they send them targeted content that prompts them to take actions (like, share, subscribe, save, or purchase).
- Users get a personalized browsing experience curated to fit their location and time zone. That's how websites like Spotify know when to say Good Afternoon.
- UX tracking helps to identify and fix bugs, enhancing user experience on the website.
How Do Businesses Benefit From Website Tracking?
Website tracking gives companies helpful information such as:
- Clickthrough/conversion rates, sections that users visit, and how they scroll
- Whether users access your website on their phones or computers
- The website's best and worst-performing pages
- Measuring the progress of marketing campaigns, e.g. email marketing
- Comparisons and analyzations website traffic
Is it Legal to Engage in Website Tracking?
For website tracking, a website collects and analyzes a user's personal data. This means that the website must first ensure end-user protection before collecting the data.
Most data privacy laws require the website to obtain the user's explicit consent before tracking their data.
What Laws Regulate Website Tracking?
The laws governing user data privacy vary depending on local laws, but governments worldwide implement these regulations to the letter.
Before your website tracks user data, you must know where most of them are to help you keep up with the local data protection laws that determine how you collect and process the users' data.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
If most or all of your website users are in the European Union, then you are automatically bound by the requirements of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) regardless of where your business is located.
The GDPR heavily insists on three data collection and processing obligations:
- End-user consent before tracking
- Provision of extensive information about your tracking process and its transparency
- User data documentation and secure storage
The GDPR has made it mandatory for websites to provide users with certain information before data is collected.
This information includes:
- The kind of data your tracking tools collect
- Your purpose for collecting the data
- Where do you send the data
- Which third-parties also access the data
- Detailed technical information about your data collection tools
California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
If your website users are within California, the site and business operations are bound by the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) as amended by the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA).
Websites must be transparent about how they collect, process and share data.
Your Privacy Policy should disclose the following:
- The kind of data collected
- The intended purpose of the collected data
- Who do you share the information with
In addition, your website's cookie banner should allow California users to opt out of the data collection process.
The cookie banner should include a "Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information" link. When any of the website's users click the link, it blocks you from collecting their data.
This process requires users to manually click the link if they wish to opt out of data collection, but users can also enable Global Privacy Control on their browser.
The GPC is a browser extension that allows website visitors to customize and set the type of data they are comfortable sharing with websites. The extension automatically notifies any website they visit about their set preferences.
Even with an enabled Global Privacy Control, all websites must allow users to opt out of data collection with a "Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information" link.
Website Tracking Policies in Brazil and South Africa
Online data protection policies in Brazil and South Africa closely resemble the EU's data protection laws and guidelines under the GDPR.
This means that the laws in these two countries insist highly on data collection transparency and explicit end-user consent.
The Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados Pessoais (LGPD) regulates business websites operating in Brazil.
The Protection of Personal Information Act (POPI) in South Africa keenly monitors your website and its operations.
How Do You Compliantly Engage in Website Tracking?
Here are some steps you can take to engage in website tracking in a compliant way.
Adopt and Implement Privacy-First Tracking Practices
Privacy-first website tracking is a user-driven data tracking process that prioritizes user privacy and data protection. These processes are designed and implemented to obtain user consent, only collect necessary data, and ensure it is secured and processed under data privacy laws.
Privacy-first compliance entails using first-party cookies that block cross-site tracking and third-party sharing. t also avoids data collection techniques like fingerprinting, which some users find overly intrusive.
Always Obtain Valid Legal Consent
Obtaining consent before engaging in website tracking is a great way to ensure you are doing so compliantly.
You can request that a user checks a checkbox or clicks a button next to an "I Agree" statement to show they are clearly consenting.
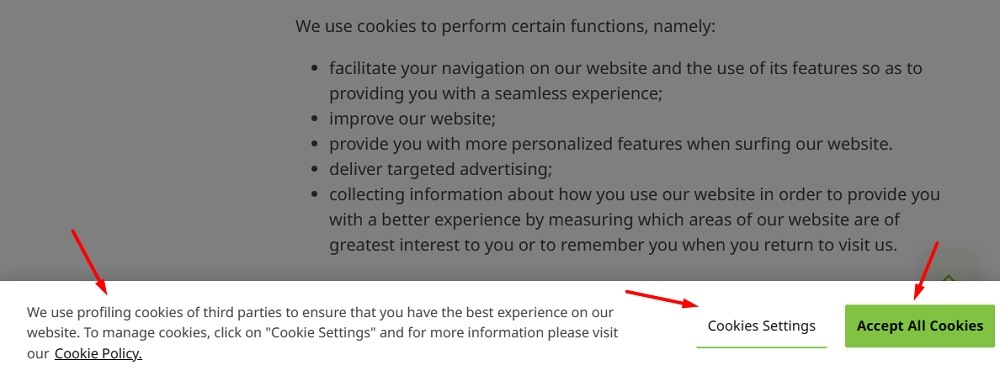
Here's an example of how consent can be requested using an "Accept" button, and how additional information can be provided, which helps make it even more clear that the user was certain about what consent was being requested for:
Store Detailed Consent Records
Documentation of user consent is important if you wish to comply with data protection laws. Neatly collect and maintain user consent forms with all the correct information, such as how the data was collected and used.
Use a Consent Management Platform
Businesses can take the extra workload off their shoulders and trust a Google-certified consent management platform that does the following:
- Employs a powerful cookie scanner
- Provides all users with the necessary information and manages the consent forms
- Properly stores user consent forms
- Auto-renews end-user consents
- Provides tools that automatically comply with various data protection policies
Summary
If you want to manage and increase your online presence, website tracking can have benefits.
Your business can get ahead of the competition by tailoring ads and content that interest your visitors/clients and get maximum conversions if you put the analytics to work.
You can fully unlock your business's untapped potential with the power of website tracking.
It is tried, tested, and approved by many businesses that started out with similar or less information.
Make sure to do this compliantly, and always request consent when possible. Become familiar with laws in your region to ensure you are following requirements.

Comprehensive compliance starts with a Privacy Policy.
Comply with the law with our agreements, policies, and consent banners. Everything is included.