If your business uses SaaS then there are specific legal requirements that you need to make sure to follow whenever you make any changes to your software or apps that affect how you handle users' privacy or personal information.
This article will explain what SaaS is, the benefits of implementing SaaS and the legal requirements for businesses that use SaaS, including how to inform users of any changes that you may make to your software or apps.
TermsFeed is the world's leading generator of legal agreements for websites and apps. With TermsFeed, you can generate:
- 1. What is SaaS?
- 2. Why You Should Use SaaS
- 2.1. Scalability
- 2.2. Maintenance
- 2.3. Access
- 2.4. Security
- 3. What Do Laws Require for SaaS Apps?
- 3.1. State Privacy Laws
- 3.1.1. California
- 3.2. Global Privacy Laws
- 3.2.1. The GDPR
- 4. How to Inform Users of Changes to Your Legal Agreements
- 4.1. Clickwrap Agreements
- 4.2. Emails
- 4.3. Blogs
- 4.4. Social Media Pages
- 4.5. Legal Page Announcements
- 5. Summary
What is SaaS?
SaaS stands for software as a service and is a way for users to access software through the internet, typically via a subscription service.
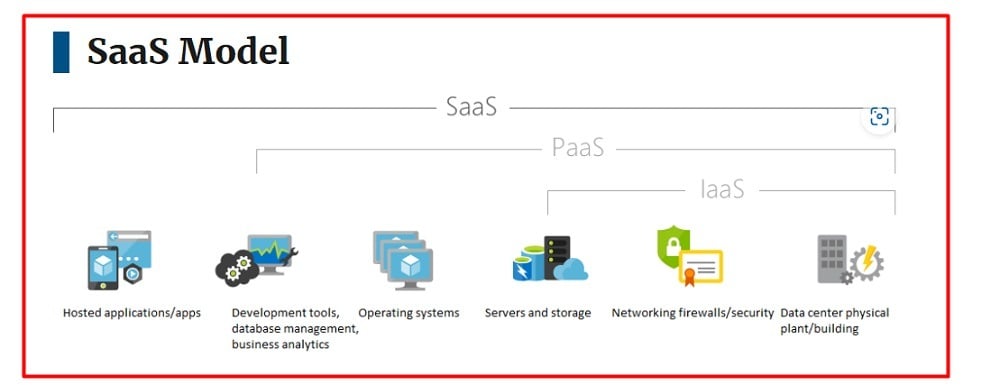
The United States government maintains a General Services Administration (GSA) website that demonstrates how the SaaS model works on its Cloud Information Center page:
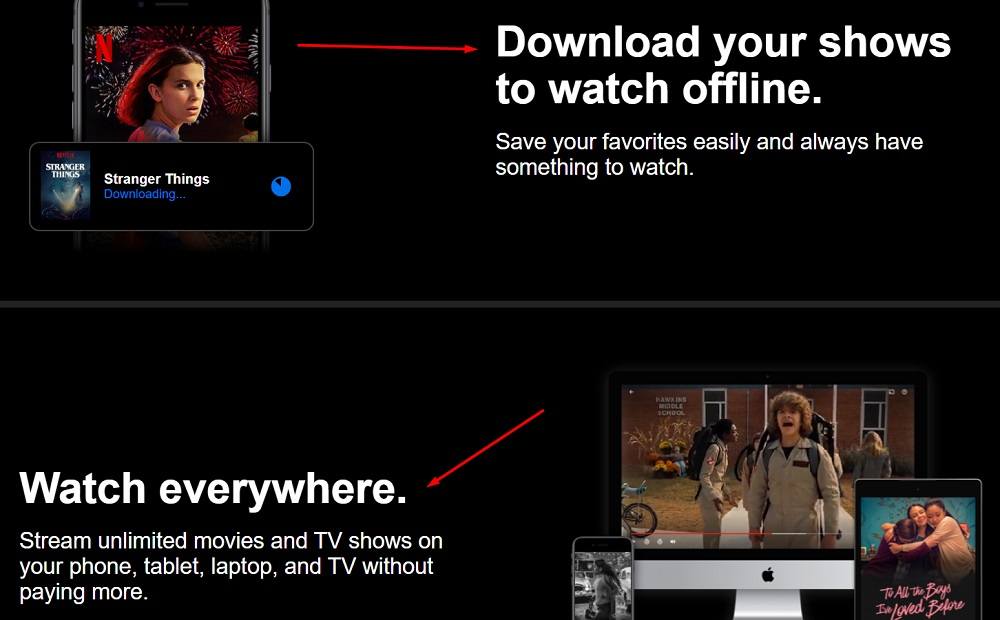
As an example, Netflix is a popular SaaS platform that provides a streaming service to its members, allowing them to download content to watch later or watch instantly online from anywhere:
SaaS is cloud-based, meaning that all of its information can be accessed over the internet, doing away with the need for users to download, install, or update software.
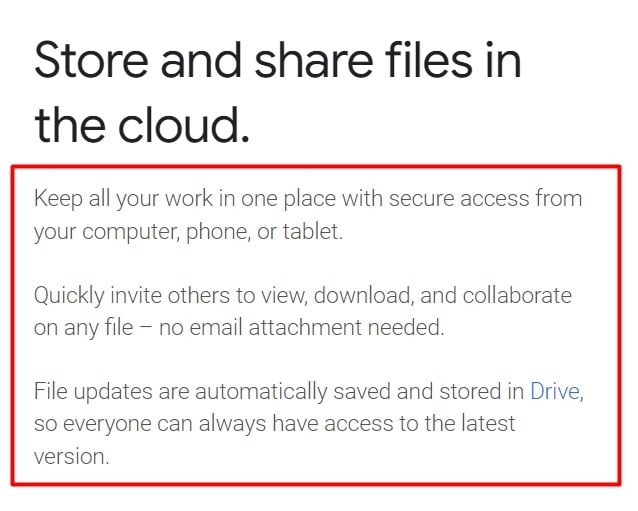
And another example is Google Workspace, which is a SaaS solution that offers users a secure method for sharing files with others and a simple way to work completely online with their team:
Why You Should Use SaaS
There are many reasons why businesses utilize SaaS, including the scalability that lowered costs and speed of installation facilitate, easy maintenance and accessibility, and security purposes.
SaaS can help you to simplify your business's processes and provides many benefits for your users, making your company's offerings more compelling to consumers looking for straightforward solutions.
Scalability
SaaS can provide users with lower licensing costs in comparison with traditional software, and can be quickly integrated. Users only need to pay for the services that they need, which is an advantage over purchasing a package at a higher cost with unnecessary features.
SaaS's lower licensing costs combined with its quick implementation can help your business to attract more clients who may not otherwise have purchased your service or product due to the prohibitive pricing of traditional software.
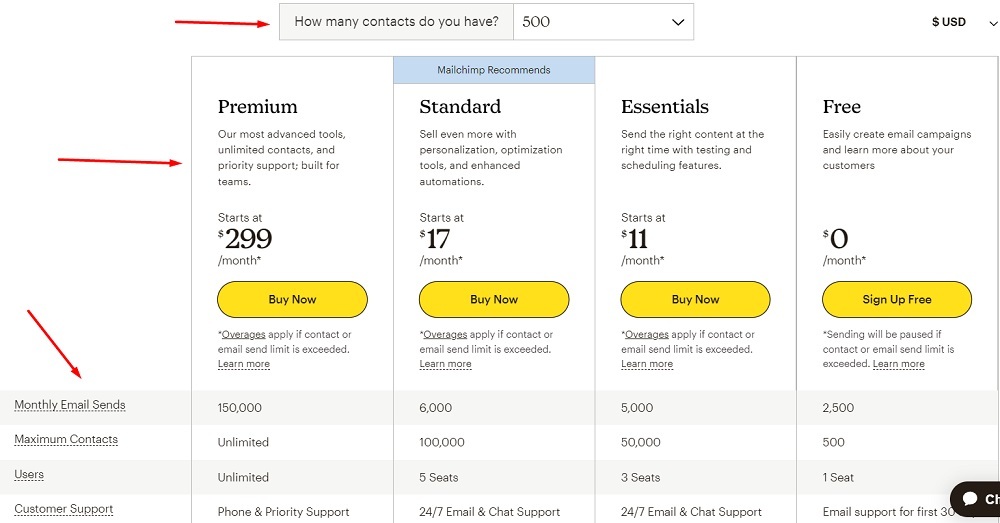
For example, Mailchimp is an email marketing SaaS that provides businesses with different plans based on how many contacts a company has, how many emails it wants to send each month, and the level of technical support it requires:
Maintenance
Users of SaaS platforms don't have to do anything special to receive updates, bug fixes, or upgrades, as those can be done over the web and the updated version of your software can be made available to all users simultaneously.
Access
SaaS is cloud-based, meaning that it is accessible from any computer or mobile device, and its intuitive design makes it easy to use.
This helps reach and connect more people regardless of location and without needing to own advanced technology devices.
Security
SaaS's ease of accessibility means that effective security measures are a must. Luckily, SaaS security practices are simple to implement. You can choose SaaS providers that offer multi-factor authentication methods and data encryption to help protect your users' accounts and personal information.
Slack is a SaaS that functions as a messaging app for businesses. Slack has many security features, one of which is the Enterprise Grid, a tool for larger organizations. Enterprise Grid owners can require their members to use a fingerprint, facial scan, or password in order to access Slack on mobile devices:

Now that you see what SaaS is and what benefits it has to offer, let's look at how laws affect SaaS platforms in a few different ways.
What Do Laws Require for SaaS Apps?

You will need to make sure that your Privacy Policy, Terms and Conditions, and any other pertinent legal agreements are in compliance with both U.S. and global privacy legislation.
For example, whenever you decide to create or add a feature to an existing product and it changes what personal information you use, or how you use it, you will need to update your policies and legal agreements to reflect any changes in the way you handle users' privacy or personal information.
That means that you will need to take a look at your Privacy Policy, Terms and Conditions, and any other legal documents and adjust them to represent the changes that have been made, as well as inform users how the changes will affect them.
State Privacy Laws
California
The California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (CCPA) went into effect January 1st, 2020, and requires certain businesses to comply with its rules. Companies that do business in the state of California and meet specific criteria in terms of annual revenue and how much of their business comes from buying and selling personal information are obligated to comply with the CCPA.
In order to remain in compliance with the CCPA, your business should:
- Inform users of their rights
- Let users know what you do with their personal information
- Keep your Privacy Policy updated
- Give users a way to opt out of third-party data sales
Otherwise, you run the risk of acquiring financial penalties of up to $7,500 for each intentional violation. Other states have similar privacy laws that you should familiarize yourself with.
To show an example of compliance with aspects of the CCPA, let's look at Microsoft Office 365. This SaaS solution provides users with different subscription services for its Microsoft Office products. In the How we use personal data section of Microsoft Office 365's Privacy Statement it explains how it uses the information it collects, which is an essential part of CCPA compliance. It informs users that the data it collects can be used to provide its products, as well as for marketing, legal, and research purposes:

Global Privacy Laws
There are numerous data protection laws in effect around the world that may apply to your company if you do business with citizens of applicable countries.
The GDPR
Europe has one of the strongest privacy laws in the form of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which requires that companies that fall under its jurisdiction do the following:
- Get users' consent before processing some types of personal data
- Keep the personal data they collect secure
- Only use or store data that is essential to doing business
Failure to comply with the GDPR can result in harsh financial penalties.
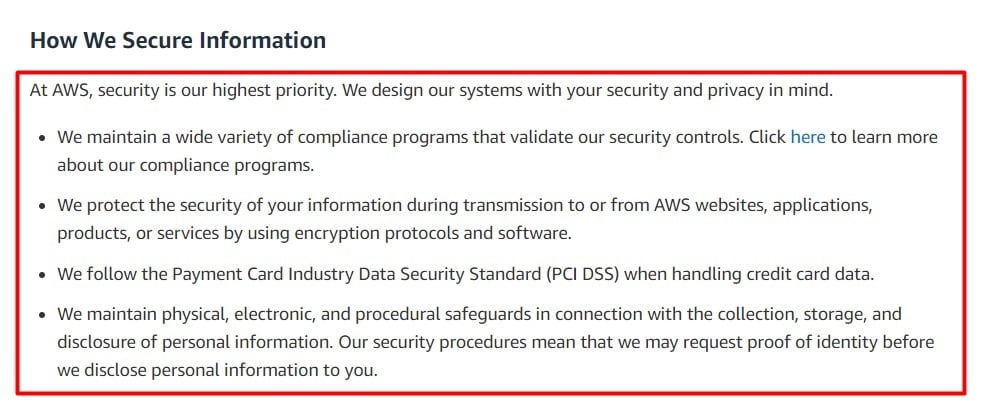
Amazon Web Services offers users cloud-based computing services that are charged based on usage. The How We Secure Information section of Amazon Web Service's Privacy Notice details what measures it takes to ensure the security of the personal information it collects and stores, helping it to stay GDPR compliant:
You should investigate the privacy laws of each country you do business with and make sure that your legal agreements contain language that keeps you in compliance with those laws.
How to Inform Users of Changes to Your Legal Agreements

Part of compliance with many privacy laws is making sure that users are made aware of any changes you make concerning users' personal information. You can use clickwrap agreements, email, blogs, social media pages, and legal page announcements to inform users anytime you update your Privacy Policy, Terms and Conditions, or any other legal agreements.
Clickwrap Agreements
It's important to make sure that users accept the conditions of use around any changes you make, which is where a clickwrap agreement can come in handy. A clickwrap agreement is a digital method for getting legal consent from users by requiring them to accept your terms before using your product or service.
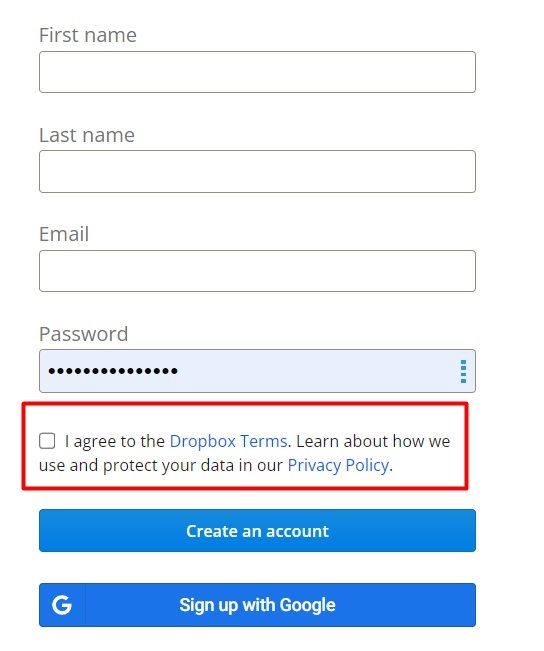
Dropbox is a file hosting platform that stores information on the cloud. Users encounter Dropbox's clickwrap agreement when they go to create an account with Dropbox, which requires that they agree to its Terms before signing up:
Emails
One way to inform users of changes to the way you handle their information is through email. You can send an email to your list, include information as part of your newsletter, or link to your Terms and Conditions and/or Privacy Policy within your email footer.
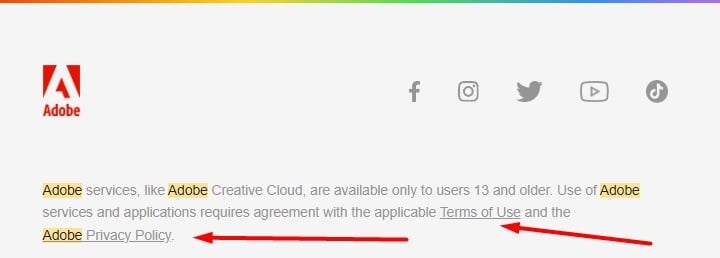
Adobe is a SaaS that creates design-related software apps. It includes an extensive footer in its emails, with links to its Terms of Use and Privacy Policy, so that users can stay up to date with any changes it makes:
Blogs
If your company maintains a blog on its website then you can use it to keep users informed of any changes you may make to your Privacy Policy or Terms and Conditions.
Dropbox uses its blog to inform users about changes to its legal agreements, including its Privacy Policy:

Social Media Pages
Using your social media pages to inform users of changes to how your business handles their information is an effective way to communicate with specific demographics.
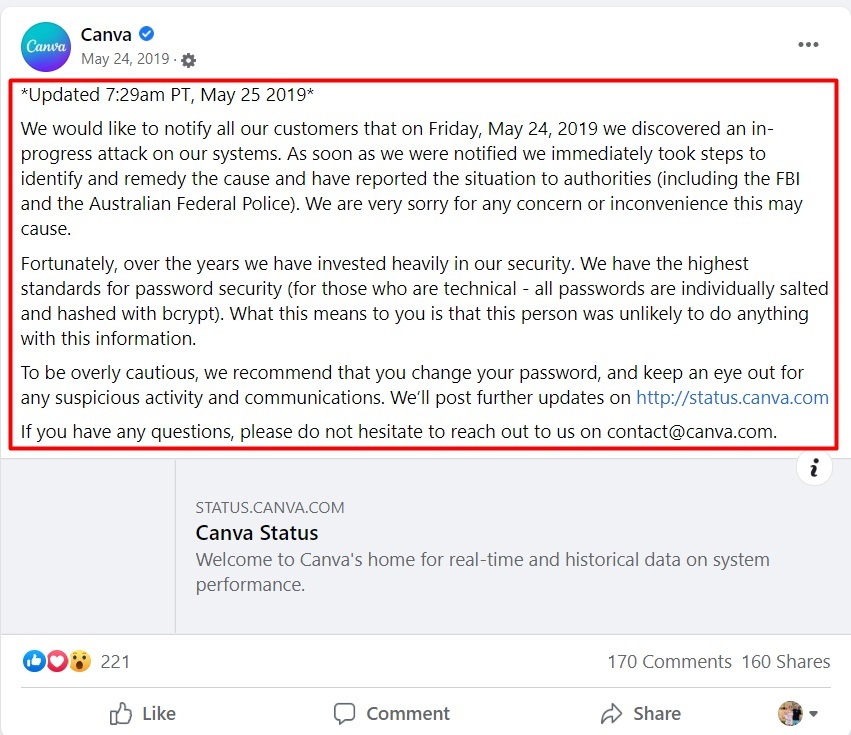
Canva is a graphic design SaaS that used Facebook to keep its users informed when its security system was jeopardized:
Legal Page Announcements
Another good place to communicate with users is on your company's legal pages.
Salesforce is a CRM Saas that added a button to its Privacy Policy page that takes users to a document outlining the ways in which it transfers data:
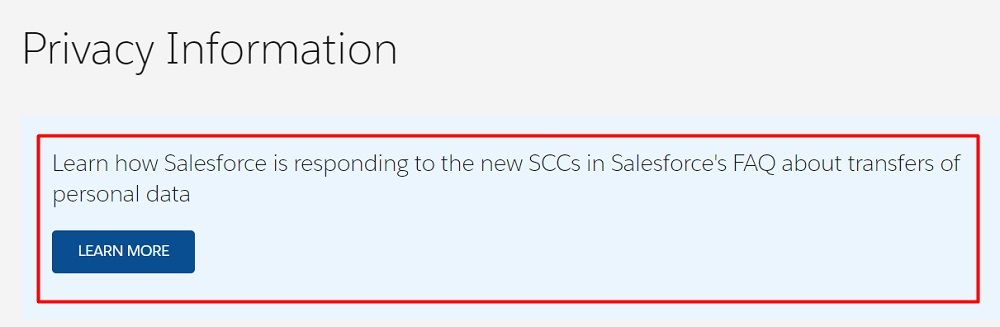
When users click on the Learn More button, they are taken to Salesforce's Data Transfer Mechanism FAQs, which details the rules and clauses it abides by when transferring users' personal information:

Summary
SaaS stands for software as a service and is a cloud-based method of providing software to users via the internet.
Many companies prefer SaaS to traditional software due to its lowered costs, speed of implementation, ease of maintenance, accessibility, security, and overall scalability.
Whenever you change or add any features to your apps or software that affect how users' privacy or personal information is handled, you will need to update your Privacy Policy, Terms and Conditions, and any other relevant legal agreements.
You should pay attention to existing privacy legislation whenever you make changes to your legal agreements, and make sure to add language that adheres to those rules.
Once you have made changes to your legal agreements, you will need to inform your users of those changes. Some efficient methods of communicating changes that affect users' personal information or privacy include email, blogs, social media pages, and legal page announcements.

Comprehensive compliance starts with a Privacy Policy.
Comply with the law with our agreements, policies, and consent banners. Everything is included.




