Under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), two or more data controllers that jointly decide why and how to process personal data are collectively known as "joint controllers."
The joint controller relationship arises more commonly than many people realize. For example, simple activities like running a Facebook Page or displaying the Facebook "Like Button" plugin on your website make you a joint controller with Facebook.
In this article, we'll look at how to define joint controllers, joint controller GDPR requirements, and how to create a "joint controller agreement." We'll be incorporating some of the recent guidance from the European Data Protection Board (EPDB).
Our Privacy Policy Generator makes it easy to create a Privacy Policy for your business. Just follow these steps:
-
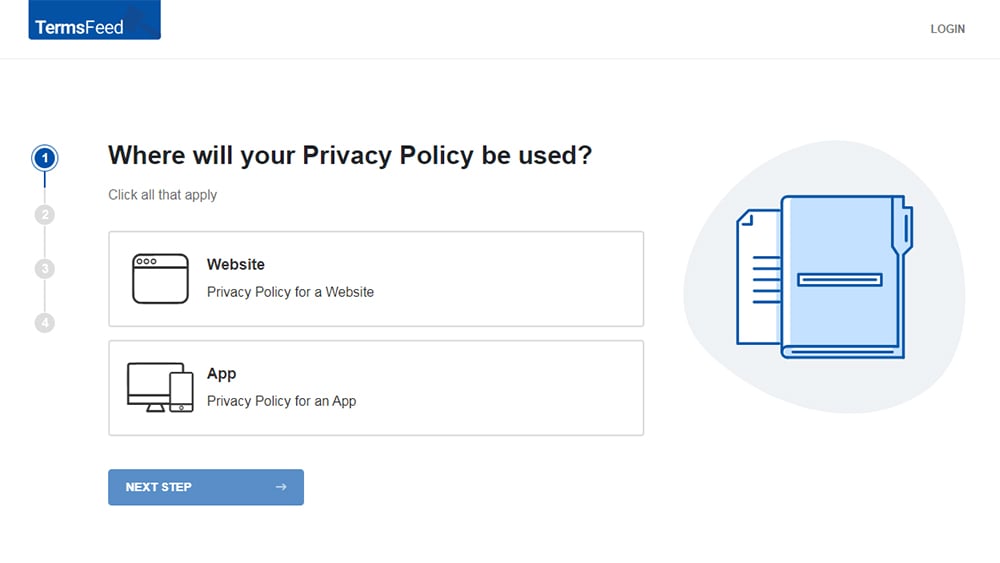
At Step 1, select the Website option or App option or both.
-
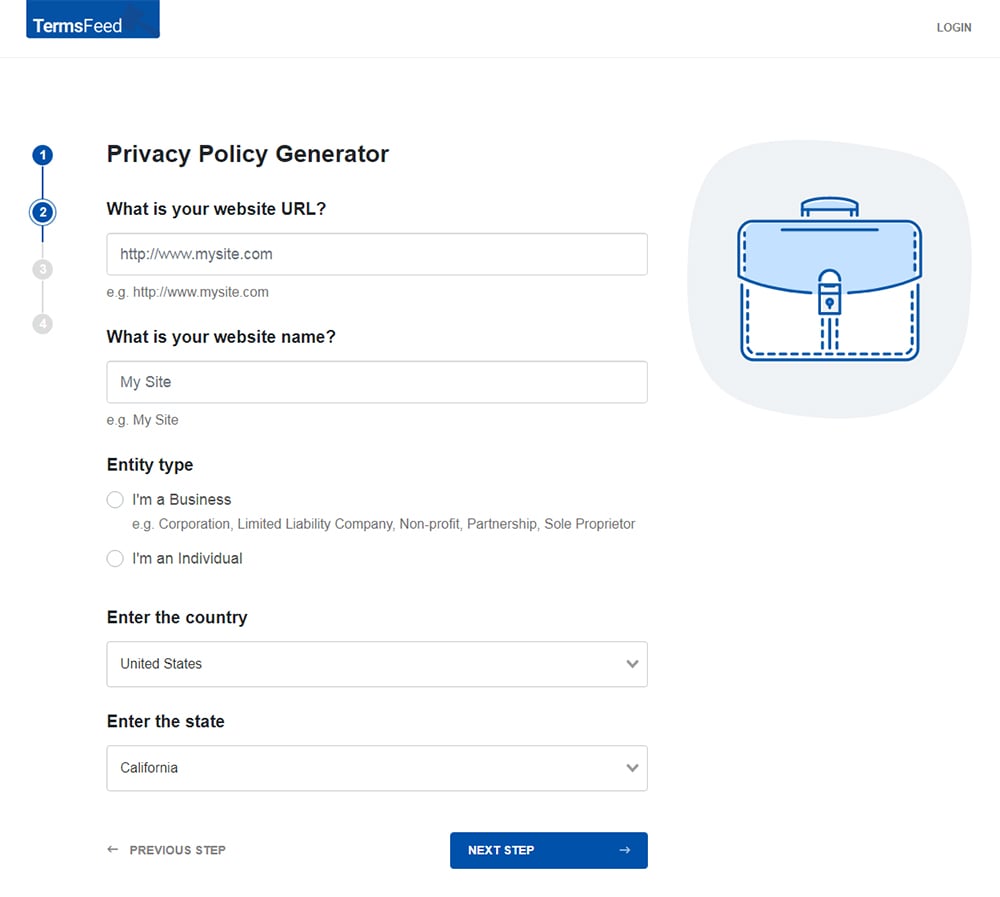
Answer some questions about your website or app.
-
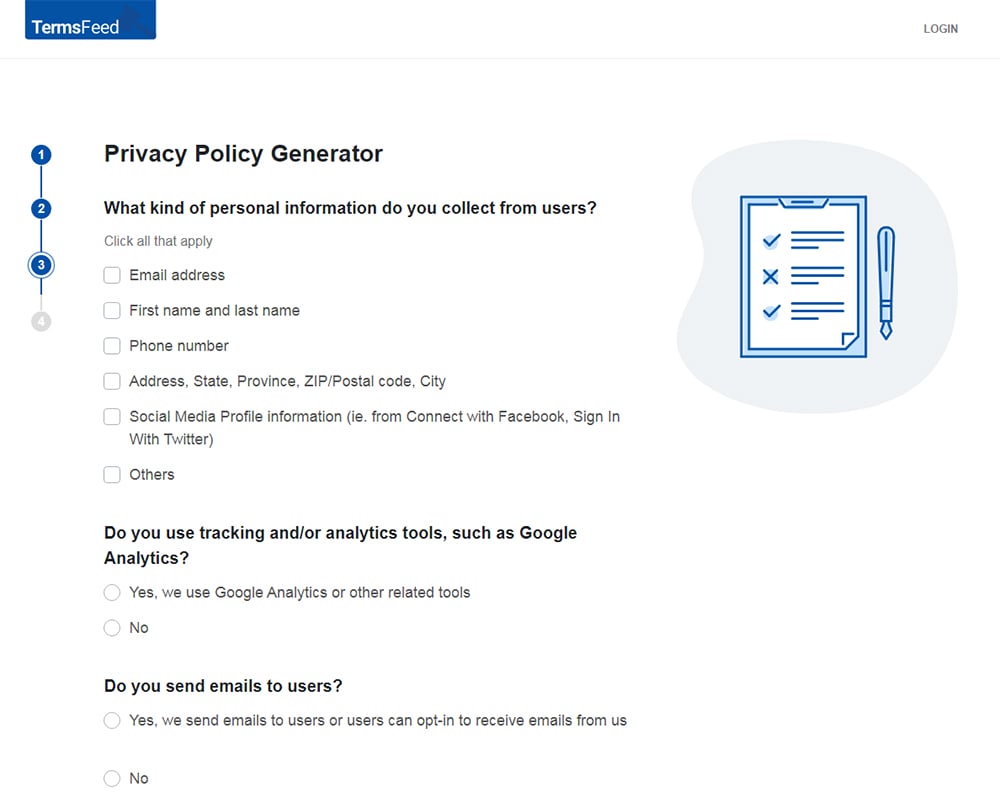
Answer some questions about your business.
-
Enter the email address where you'd like the Privacy Policy delivered and click "Generate."
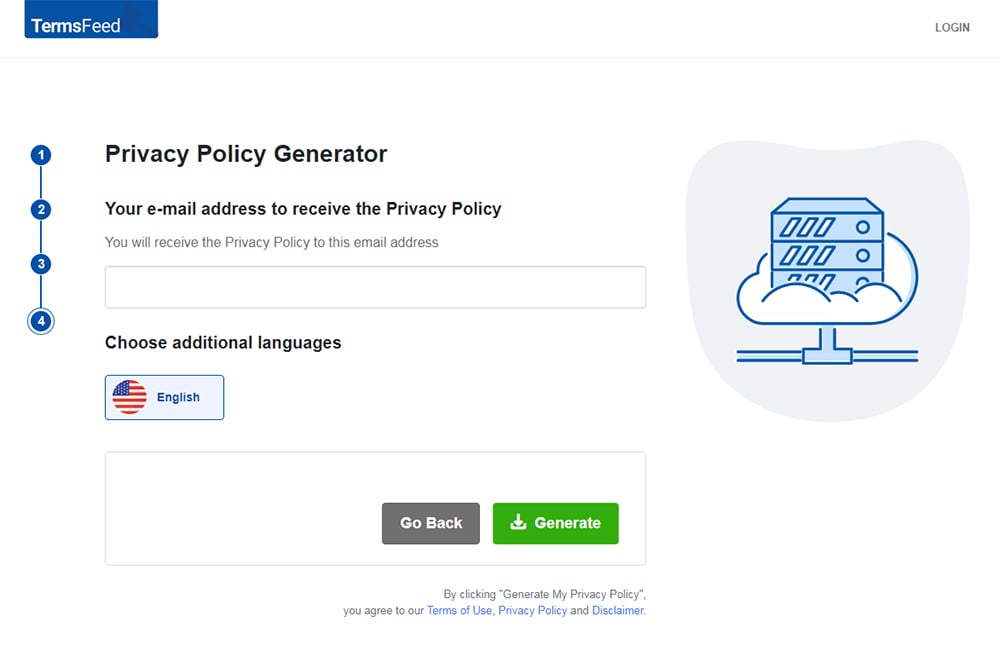
You'll be able to instantly access and download your new Privacy Policy.
- 1. What are GDPR Joint Controllers?
- 1.1. GDPR Controllers
- 1.2. GDPR Joint Controllers
- 1.3. GDPR Joint Controllers vs. GDPR Controller and Processor
- 2. Examples of GDPR Joint Controllers
- 2.1. Facebook Pages
- 2.2. Facebook "Like" Button
- 2.3. Joint Research Project
- 2.4. Combined Services
- 3. GDPR Joint Controller Agreement
- 3.1. Facebook Page Insights Controller Addendum
- 3.2. Facebook Controller Addendum
- 3.3. CAO Joint Controller Agreement
- 4. Summary
What are GDPR Joint Controllers?
To help you understand joint controllers, we need a quick refresher on the GDPR's definition of a "controller."
GDPR Controllers
Most of the GDPR's provisions are aimed at "data controllers" (controllers). Here's a quick re-cap on controllers, at Article 4 (7) of the GDPR:

A controller:
- Can be any type of "person," including an individual, business, charity, or public authority
- "Determines the purposes and means of the processing of personal data:" decides why and how to process personal data
For example, when Amazon personalizes recommended items based on previous purchases, it is acting as a controller.
- The "personal data" includes information about previous purchases, a customer ID, and other technical information.
- The "purposes" are to deliver a personalized shopping experience and target ads.
- The "means" involve processing personal data using an algorithm to determine which products to recommend.
GDPR Joint Controllers
Here's the GDPR's definition of "joint controllers," at Article 26:

A joint controller is a member of a group of controllers that "jointly determine the purposes and means of processing."
Article 26 also tells us that:
-
Joint controllers must create a "joint controller agreement" (this is our term, rather than the GDPR's) which sets out their respective responsibilities for GDPR compliance, including:
- Who is responsible for facilitating data subject rights requests
- Who will create a Privacy Policy and provide other relevant privacy notices to data subjects
- Joint controllers "may" designate a single point of contact for data subjects
- The "essence" of the written joint controller agreement must be made available to data subjects
- Regardless of who is responsible for which aspects of GDPR compliance, data subjects may exercise their GDPR rights against any of the controllers
GDPR Joint Controllers vs. GDPR Controller and Processor

The relationship between joint controllers is very different from the relationship between a controller and a data processor.
Here's how the two types of GDPR relationships compare:
| Joint controllers | Controller and processor | |
| Determining the purposes and means of the processing of personal data | Each group member determines the purposes and means of the processing of personal data. | Only the controller determines the means and purposes of the processing of personal data. The data processor processes personal data on the controller's behalf. |
| Allocating GDPR duties | The group members can decide their respective roles and responsibilities among themselves. | The roles and responsibilities of the data processor are strictly defined at Article 28 of the GDPR. |
| Written agreement between parties | The group members must create a transparent "joint controller agreement" that is made available to data subjects. This joint controller agreement does not have to be a legally-binding contract. | The controller and the data processor must create a "data processing agreement," containing mandatory clauses that set out the scope of the processing, the duties of the processor, the processor's security standards, etc. The data processing agreement is a legally binding contract. |
| Liability of each party | All group members are liable to data subjects for any GDPR violations that arise out of the processing. | Processors are only liable for violating their data processing agreement or violating the limited number of direct processor responsibilities under the GDPR. |
For more information, see our article: GDPR Procedures for Data Controllers and Data Processors.
Examples of GDPR Joint Controllers

The types of activities that might give rise to a "joint controller" relationship include:
- Two or more controllers collaborating on a project that requires the processing of personal data (the same processing operation for the same purposes)
- Two or more controllers separate processing purposes that are "closely linked or complementary"
Here are some real and hypothetical examples of the joint controller relationship.
Facebook Pages
In 2018, a case at the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) found that Facebook is in a joint controller relationship with Facebook Page admins when they use Facebook's "Page Insight" tool.
- Facebook Pages (previously called "Fan Pages") are operated by companies (and other entities) wishing to promote themselves on Facebook.
- Facebook's Page Insight tool uses cookies to measure users' interactions with a Facebook Page.
- Facebook delivers anonymized usage statistics to Page admins via its Page Insight tool.
- The types of cookies used by Page Insights involve the processing of personal data.
Here are some of the reasons that the CJEU decided that Facebook and Facebook Page admins are joint controllers:
-
Facebook and Page admins process the personal data collected by these cookies for different (but closely linked) purposes:
- Facebook's purpose is to improve its ad targeting.
- The Page admin's purpose is to learn about how people interact with its Facebook Page.
- The relationship between Facebook and the Facebook Page admin is not a controller/processor relationship, because both parties have a distinct interest in the processing and are pursuing their own purposes.
- While the statistics generated by Page Insights are anonymized, this doesn't prevent the Facebook Page admin from being a controller.
The upshot of this is that:
- Facebook and Facebook Page admins must come to an arrangement to determine who is responsible for which aspects of GDPR compliance (this is the "Page Insights Controller Addendum," which we will look at below).
- Facebook Page admins are jointly liable with Facebook for any GDPR violations arising from the processing of personal data via the Page Insights tool.
- Data subjects who have visited a Facebook Page can submit data subject rights requests to either Facebook or the relevant Facebook Page admin.
For more information, see our article: Privacy Policy for Facebook Pages.
Facebook "Like" Button
In 2019, another CJEU ase determined that where a website operator displays the "Facebook Like Button" plugin on its website, it enters into a joint controller relationship with Facebook.
- The Facebook Like Button plugin allows a logged-in Facebook user to "like" the website operator's Facebook page.
- The plugin uses cookies to transfer personal data (including the user's IP address and browser string) from the website to Facebook.
- Facebook and the website operator are using the Facebook Like button to process personal information for different (but closely linked) purposes.
The upshot of this is that:
- Facebook and website operators must come to an arrangement to determine who is responsible for which aspects of GDPR compliance (this is the "Controller Addendum," which we will look at below).
- Website operators are jointly liable with Facebook for any GDPR violations arising from the processing of personal data via the Facebook Like Button.
- Website operators using the Facebook Like Button must have a valid lawful basis for processing and must notify data subjects of how their personal data will be processed (the CJEU decided that this duty fell on the website operator rather than Facebook).
Joint Research Project
In this hypothetical example, three companies decide to undertake a study on workplace stress among their employees. Employees from each company can participate in a survey and the data is combined to create a report.
Each of the three companies is a controller, responsible for:
- Conducting the survey among its employees
- Informing employees about the nature of the study, and how data will be shared among the three companies
- Obtaining consent from participating employees
- Ensuring the personal data is processed with an appropriate degree of security
- Sharing its results among the group members
The companies' joint controller agreement should set out the roles and responsibilities of each group member, including:
-
Who is responsible for creating privacy notices and providing them to data subjects:
- This is likely to be a joint responsibility between all parties
-
Who is responsible for facilitating data subject rights:
- Each company is likely to facilitate the data subject rights of all employees
- Employees may exercise their data subject rights against any of the three companies
-
How personal data will be processed to produce the final report:
- One company might decide to take the lead on this
-
How personal data will be erased once the study is complete:
- For example, each company must ensure it erases the personal data in its possession, including any personal data it has received from other companies
Combined Services
Here's an example provided by the European Commission of how a joint controller relationship can arise between two companies offering "combined services."
- Company A offers babysitting services online
- Company B offers DVD rentals online
- Company A and Company B collaborate to offer combined services
- Using Company A's website, parents can hire a babysitter and rent DVDs for the babysitter to bring to their homes
- The companies share clients' personal data
The European Commission says that Company A and Company B are joint controllers because "not only do they agree to offer the possibility of 'combined services' but they also design and use a common platform."
GDPR Joint Controller Agreement

Joint controllers must divide their GDPR compliance responsibilities "in a transparent manner" via what we're calling a "joint controller agreement." The "essence" of this arrangement must be made available to data subjects.
Remember that this joint controller agreement doesn't have to be a contract. However, it can form part of a contract, and joint controllers may wish to enter into a contract to establish the extent of each party's liability.
Let's look at some joint controller agreements to see how controllers approach this GDPR duty.
Facebook Page Insights Controller Addendum
When the CJEU decided that Facebook and Facebook Page admins were joint controllers, Facebook had to act to ensure it was complying with Article 26 of the GDPR. This meant setting up a joint controller agreement with Page admins.
To this end, Facebook created its Page Insights Controller Addendum. Here's an excerpt from this joint controller agreement:

There are some important things to note about this agreement:
- Facebook's Page Insights Controller Addendum is legally-binding. Page admins have to agree to it.
-
Facebook takes on almost all of the GDPR's responsibilities, assigning only the following duties to Page admins. A Page admin must:
- Ensure there is a lawful basis for processing Page Insights data
-
Comply with Article 13 (1) (a-d) of the GDPR by providing notice (e.g., via a Privacy Policy) of:
- Contact details
- Contact details for a Data Protection Officer (if relevant)
- Its purposes and lawful basis for processing Insights data
- Details of its legitimate interests for processing (if relevant)
- Forward any data subject rights requests to Facebook within seven days
-
Additional clauses in the Addendum include:
- Facebook assumes responsibility for data security
- Ireland's Data Protection Commission is the lead Data Protection Authority
- Any legal disputes arising out of the joint controller relationship will be resolved in the Irish courts
Facebook Controller Addendum
Facebook's Controller Addendum covers any of its products that transmit "Business Tools Data," including the Facebook Like Button plugin.
The Addendum includes a table that designates GDPR responsibilities:
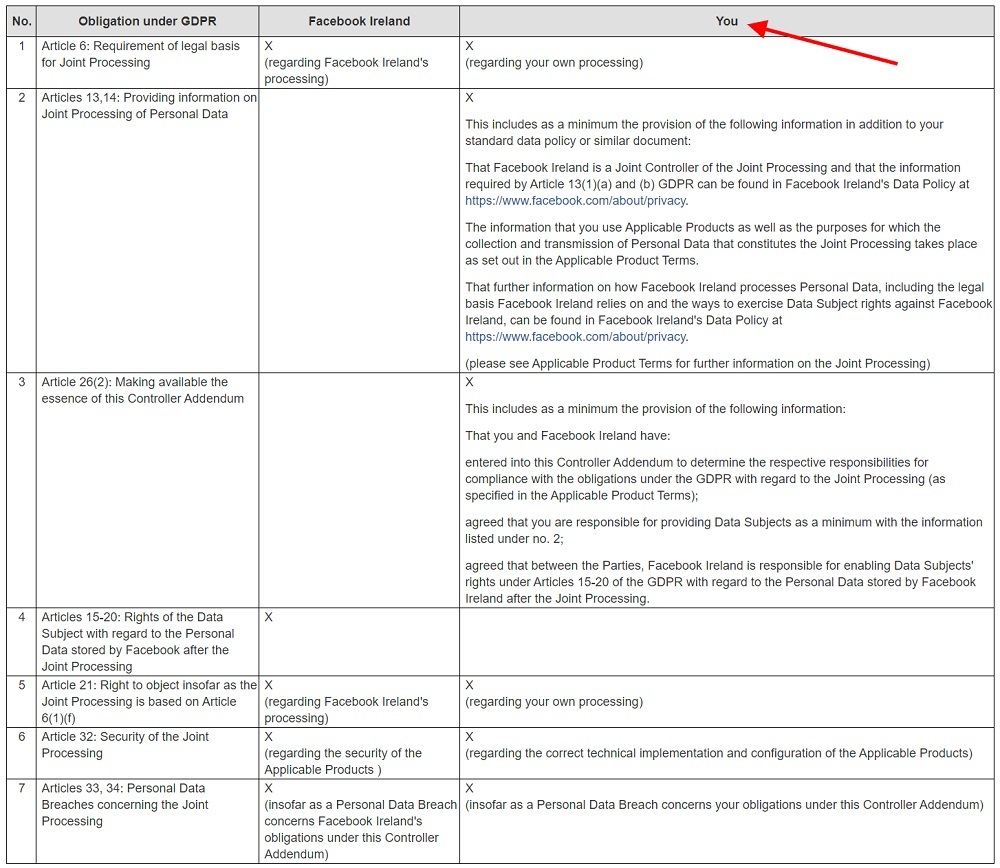
Website operators must comply with the following parts of the GDPR:
- Establishing a lawful basis for processing
- Making the joint controller agreement available to data subjects (e.g., via clauses in a Privacy Policy)
- Complying with requests under the "right to object"
- Securing personal data received/transmitted by the Facebook Like Button
- Complying with the GDPR's data breach notification rules
CAO Joint Controller Agreement
Here's an example of a joint controller agreement between Ireland's Central Applications Office (CAO) and the Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) with which CAO jointly processes personal data.
This excerpt from the agreement shows how the two controllers divide up some of the GDPR's responsibilities:

In the above excerpt, we can see that:
- CAO will facilitate data portability requests unless the HEI holds the personal data requested
- CAO will provide a Privacy Policy that covers the joint processing activity
- Both parties are responsible for implementing data security
- Both parties will inform each other about data breaches at the same time as notifying the Data Protection Authority
Summary
-
A joint controller relationship arises where two or more controllers jointly determine the purposes and means of the processing of personal data. This might be because:
- They are processing personal data for the same purpose
- They are processing personal data for closely linked or complementary purposes
-
Joint controllers must create a "joint controller agreement." This agreement:
- Does not need to be legally binding
- Must determine which controller is responsible for which aspects of GDPR compliance
- The essence of the joint controller agreement must be made available to data subjects
- Data subjects can exercise their data subject rights against any of the controllers
- Each joint controller is liable for any GDPR violations arising out of the joint controller relationship

Comprehensive compliance starts with a Privacy Policy.
Comply with the law with our agreements, policies, and consent banners. Everything is included.




