Terms & Conditions (T&C) are also referred to as Terms of Service and Terms of Use. This document is a contract between you and your users so you can assure appropriate use of your app and website.
While you may be distributing an app or website as an individual developer rather than as a company, this does not mean you will not benefit from drafting T&C. This allows you legal protection and maintains the functioning and reputation of your app or website.
This article explains why individuals need a Terms and Conditions agreement, and what one should contain.
Our Terms and Conditions Generator makes it easy to create a Terms and Conditions agreement for your business. Just follow these steps:
-
At Step 1, select the Website option or the App option or both.
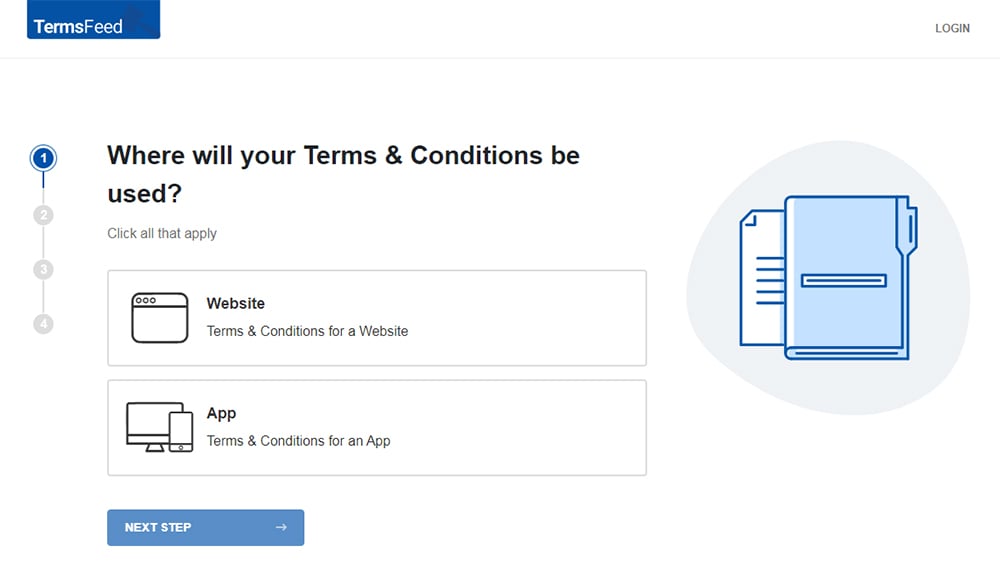
-
Answer some questions about your website or app.
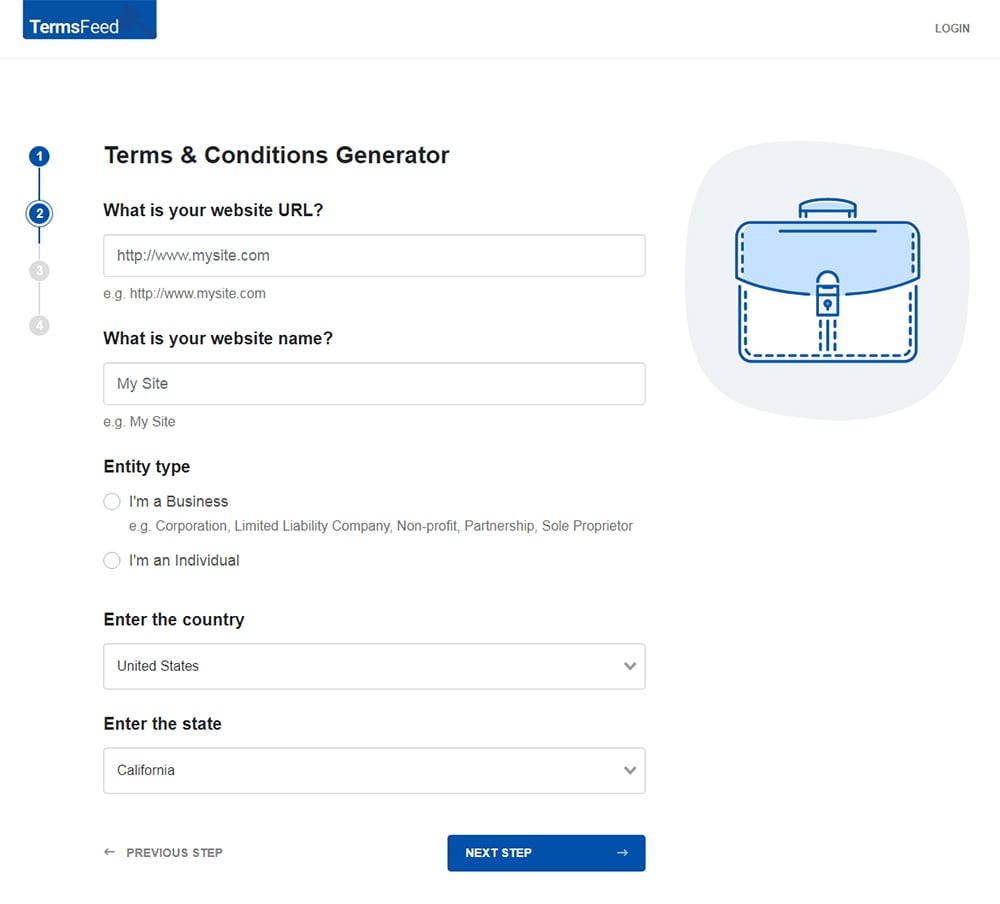
-
Answer some questions about your business.
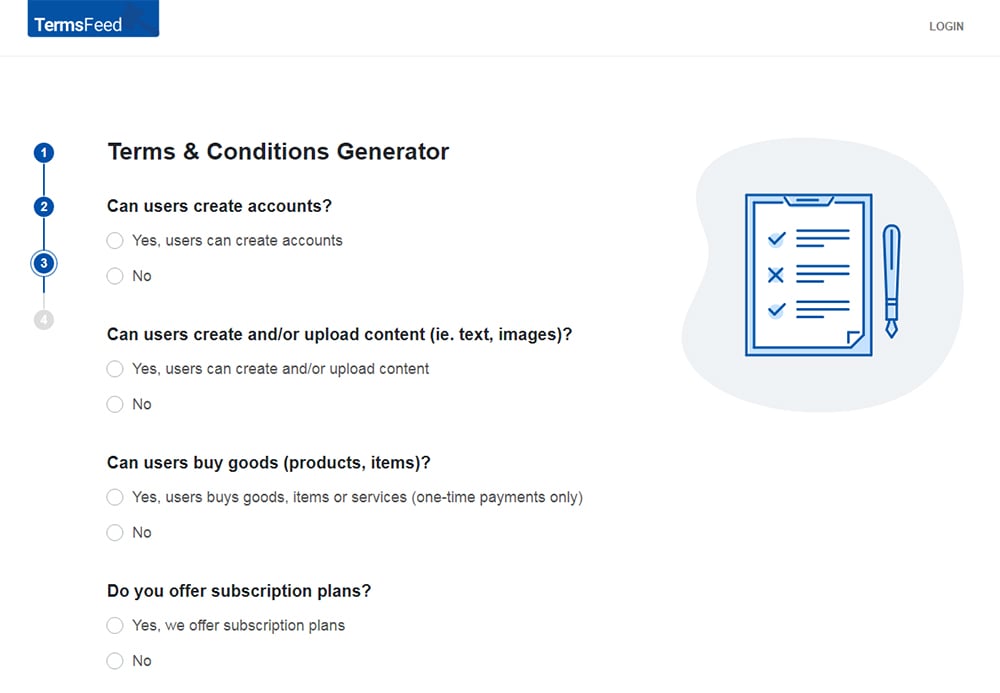
-
Enter the email address where you'd like the T&C delivered and click "Generate."
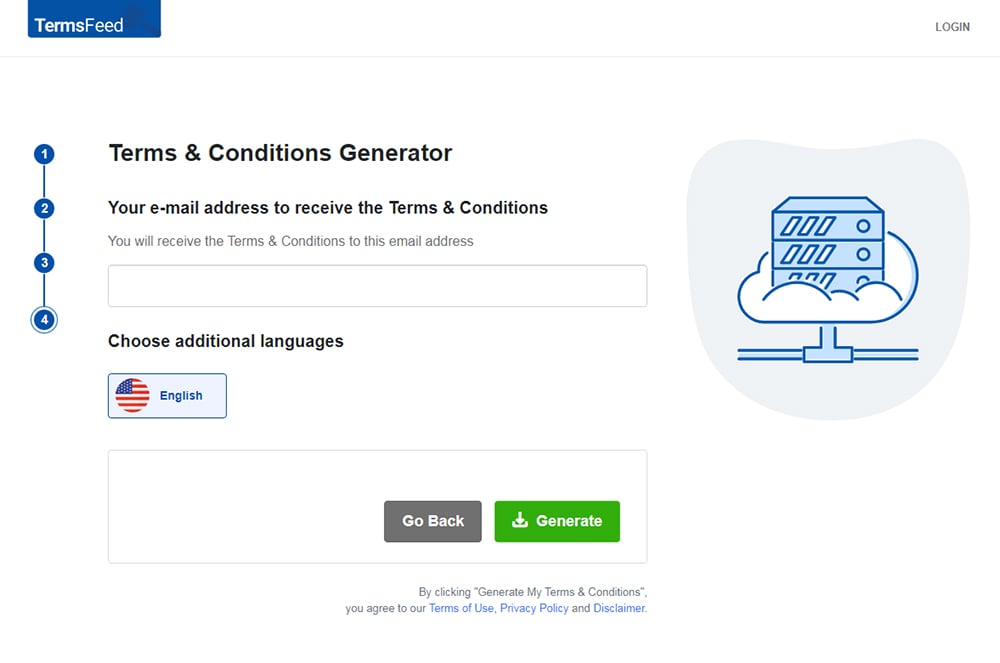
You'll be able to instantly access and download the Terms & Conditions agreement.
- 1. What is a Terms and Conditions Agreement?
- 2. Why Do Individuals Need Terms and Conditions?
- 3. Is Having Terms and Conditions a Legal Requirement?
- 4. Why Should an Individual Have a Terms and Conditions Agreement?
- 5. What Information Should a Terms and Conditions for Individuals Contain?
- 5.1. What Behaviors are Not Allowed
- 5.2. Protection for Your Intellectual Property
- 5.3. How and When Accounts Can be Terminated
- 5.4. Limits to Your Liability
- 5.5. What is the Governing Law
- 6. Where Should You Display Your Terms and Conditions Agreement for Individuals?
- 7. How Do You Get Individuals to Agree to Your Terms and Conditions?
- 8. Summary
What is a Terms and Conditions Agreement?
A Terms and Conditions agreement is a legal document that outlines important aspects of the relationship between you and your end users/customers, etc.
The agreement will address points such as governing law, limits in legal liablity, how pricing and refunds are handled, how accounts can be terminated and so on.
Why Do Individuals Need Terms and Conditions?
Drafting a T&C agreement when you are transacting business as an individual offers you protection and enforcement powers that may not be available if you proceed without one.
Typically, apps and websites are owned by companies, not individuals. This is true even when a product or service is marketed primarily under an individual's name.
Tim Ferriss is known for his productivity products. His website brands primarily feature his name and a reference to his podcast, The Tim Ferriss Show:

However, when you visit his T&C, you see something different. His terms refer to an entity and not to him personally:

The primary reason for this preference is because it creates personal liability protection. If you place the responsibilities listed in the T&C in the hands of a company, a user who feels wronged can only sue your company - not you personally.
However, when you present the T&C in your name, it allows a user to hold you personally responsible for breaches. You can lose assets and face fines that are enforceable against your personal accounts rather than the ones you set aside only for business transactions.
While this sounds like creating T&C as an individual would leave you more vulnerable to liability, the opposite is true.
Is Having Terms and Conditions a Legal Requirement?
A T&C is not required by law in any jurisdiction.
Why Should an Individual Have a Terms and Conditions Agreement?
Here are some reasons why having a T&C is important for individuals as well as businesses alike.
- Creates a legally binding contract
- Prevents abuses
- Protects intellectual property
- Allows you to terminate abusive accounts
- Limits your liability
What Information Should a Terms and Conditions for Individuals Contain?
Here are some basic, general clauses that every Terms and Conditions agreement can benefit from. While yours may differ in content, the following examples will help you understand how to create your own clauses.
What Behaviors are Not Allowed
Abusive use of your app includes harassing behavior like derogatory content, spamming other users, and stealing intellectual property. Part of your T&C should list what is not allowed on your app.
This is especially important if your website or app encourages interaction between users and user-generated content. You will lose followers if people do not feel safe using your service.
As a dating app, Tinder contains many opportunities for abuse by unscrupulous people. That is why the rule section in its T&C is long and detailed. It contains behavioral limits but also the usual restrictions against spamming and infringing on intellectual property:
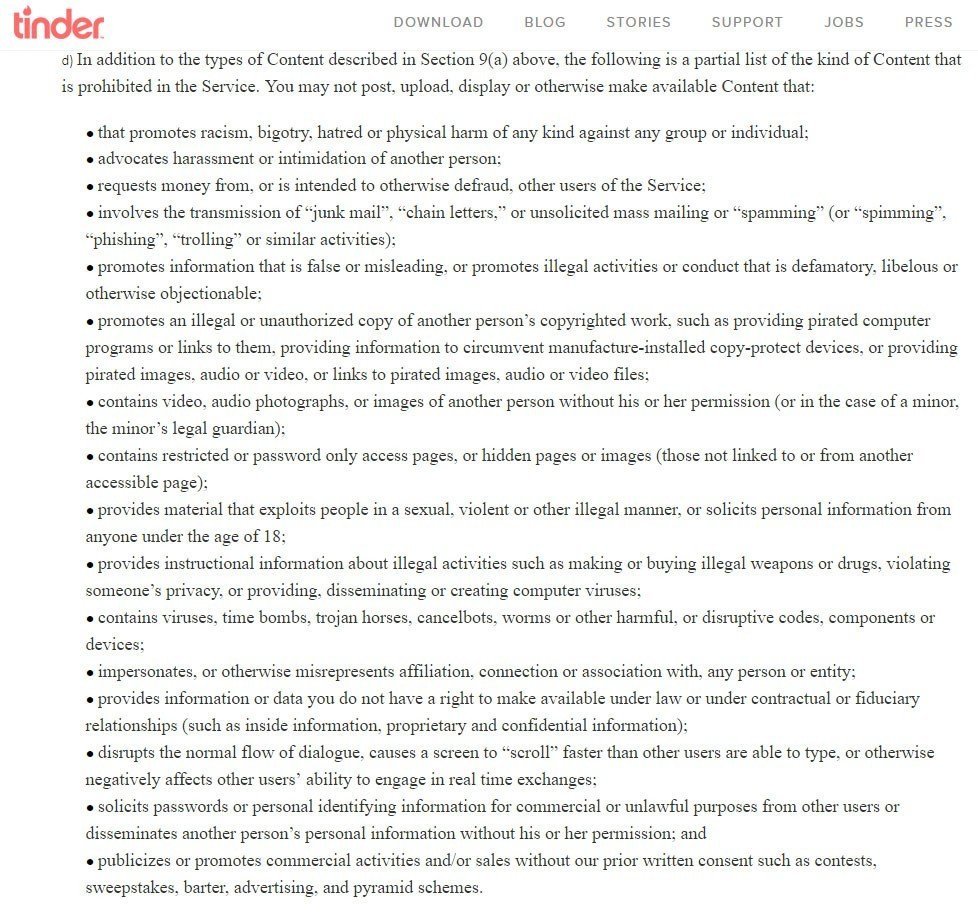
Your rules will depend on the purpose of your app and the potential of abuse. At the very minimum, you want to prevent the following:
- Privacy breaches
- Spamming of users
- Infecting your system with viruses
- Intellectual property infringement
- Inappropriate commercial activities
Protection for Your Intellectual Property
Your app or website likely contains unique graphics, content, logos, and other items that are unique to you and the brand you are building. If your app or website is a game, there is likely music, storylines, characters, and unique elements to your game that you do not want other developers copying.
Users may attempt to steal these elements, too. For that reason, your T&C must contain provisions that protect your intellectual property. These usually state these items belong to you and infringement may result in damages against the user and account termination.
FIFA, which owns several trademarks, makes this clear in its T&C:

Intellectual property infringement affects everything that makes your web site or app unique. Your T&C makes your ownership of these elements clear and gives you power to enforce those rights against users if they commit infringement.
How and When Accounts Can be Terminated
The most common enforcement measure for a T&C is the ability to terminate accounts. That action allows you to remove problematic users and keep your online community safe and free from infringement.
Sometimes the Rules for Use and the Termination Clause occupy the same section in the T&C. The easiest way to approach this as an individual is to draft a general termination clause.
For example, Envato Market explains that a breach of the T&C is cause for account termination:
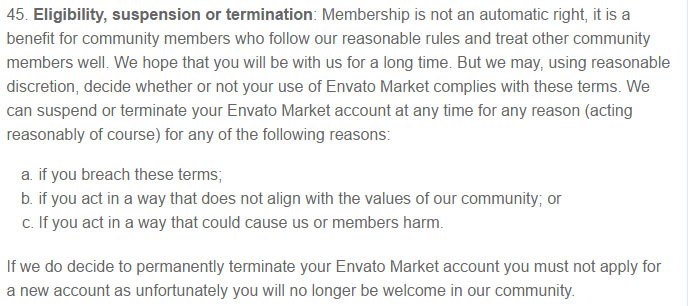
Notice that the termination clause grants broad discretion. This allows you to address scenarios you never anticipated and handle these matters on a case-by-case basis. If this is the first time you're releasing an app or website, broad discretion is the best approach.
Limits to Your Liability
The best way to reduce your liability is by incorporating your development efforts instead of holding yourself out as an individual. If incorporating is not practical, then liability limitation clauses in your T&C become even more essential.
Many of these provisions address damages a user may face if your app or website shuts down. If you run accounting, development or customer service platforms, a failure on your end can be devastating to a user. However, since many of these events occur through no fault of your own, it is a good idea to disclaim your liability.
BCS waives liability as to content quality, technical difficulties, and other contingencies through its liability disclaimer section:

You must assess which risks arise from the use of your app. While you cannot waive liability for privacy breaches, you can and should disclaim losses and damages caused by viruses, technical failure, and any other losses incurred by users or third parties as a result of using your app or website.
What is the Governing Law
You do not want to be dragged into a court in Singapore if you conduct business in Nashville, Tennessee. Adding a governing law provision prevents that by limiting dispute resolution to your local jurisdiction.
A governing law provision or clause is a clearly-stated section that's meant to make things easier for you.
Here's an example of a clause that requires disputes to be filed in Santa Clara County as consistent with California law:

Do not make this a general, e.g. "Only the laws of the United Kingdom will apply." You could be dragged all over your home country and if that is in Russia or the United States, that could add expensive and burdensome travel on top of your legal challenges. Choose the laws and court most local to you and be specific about it in this clause.
Developing a website or apps as an individual does not preclude you from responsibilities or challenges faced by corporate entities.
You will find it easier to transact business and preserve the character of your website or app by drafting a Terms & Conditions agreement. Individual developers need them as much as companies do, and in some instances - like avoiding personal liability - may need them even more.
Where Should You Display Your Terms and Conditions Agreement for Individuals?
Display a link to your Terms agreement at least in your website's footer. Another common place is when users sign up for an account with you, or make a purchase.
The website footer link ensures that users can view the agreement at any time, while the other areas present the agreement at the point when a contract is formed between you and the user by way of some action (making a purchase, signing up for an account on your site, etc.).
Here's an example of a Terms agreement link displayed in a website's footer:
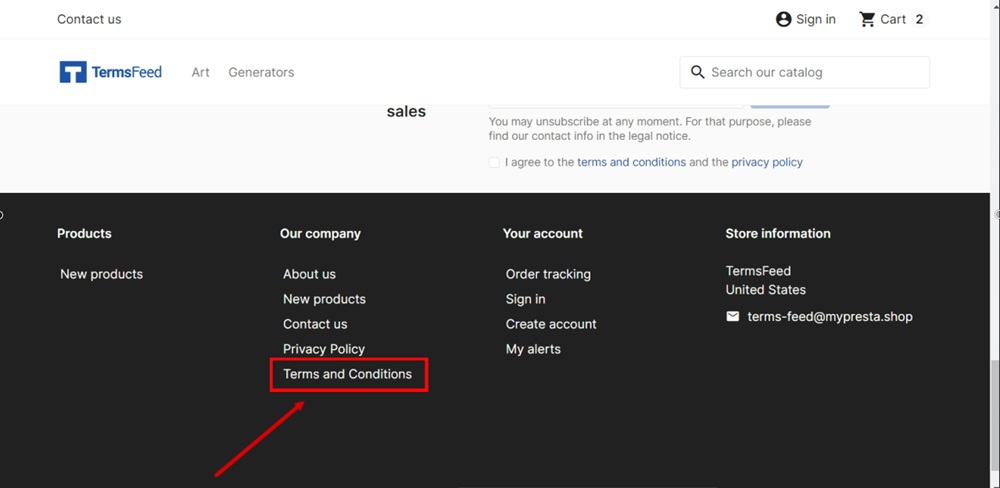
And here's a way you can present your Terms link when users are signing up/creating an account:
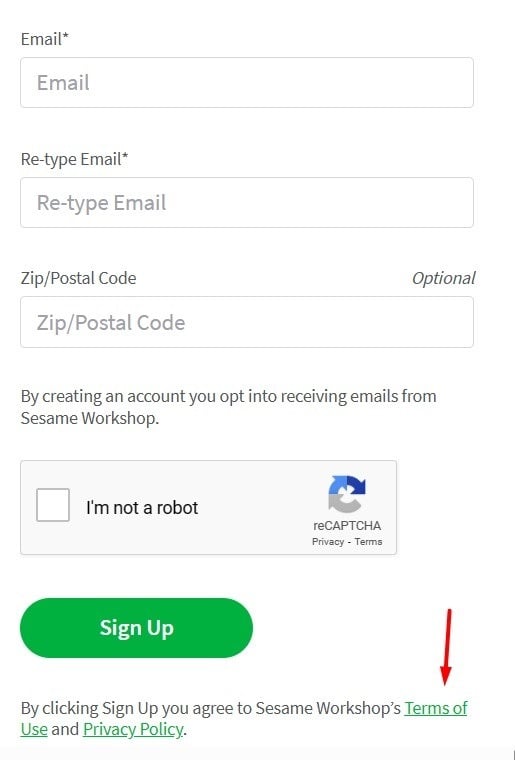
How Do You Get Individuals to Agree to Your Terms and Conditions?
The most common way to assure acceptance of your T&C is through clickwrap. This requires acceptance of the terms before a user is allowed to establish an account and use your app or website.
A common best practice way to do this is to use an "I Agree" checkbox. Users must click the box to proceed, and the box is next to a statement that makes it clear that by checking it, the user is agreeing to your Terms.
You see it at sign up as shown through this example with Gazelle, an online electronics marketplace:
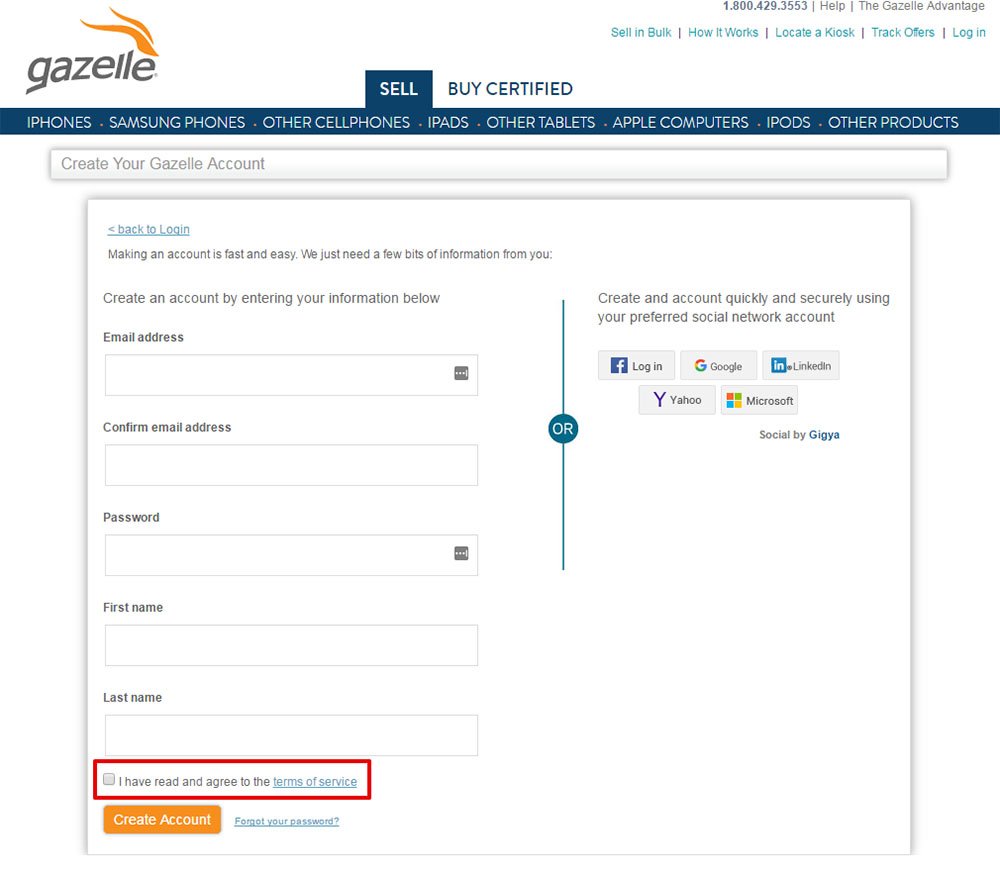
And here's one more example:
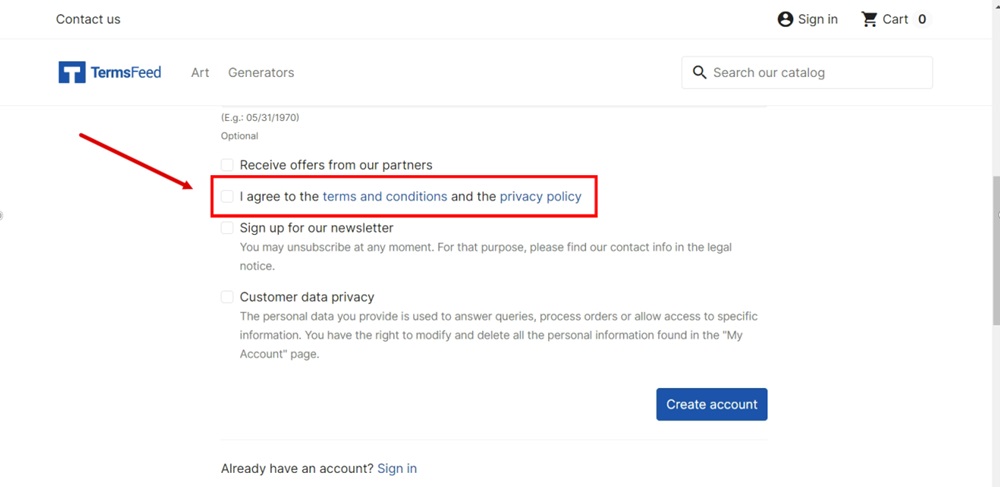
Summary
If you're operating a website or blog as an individual versus a company, you still should have a Terms and Conditions agreement. While not a legal requirement, the benefits will be exceptionally useful for you when running your site or service.
Your Terms and Conditions agreement is where you can include important information to limit your legal liability, set your governing law, put forth the rules of using your site or service, what will be grounds for termination of accounts, and so forth.
Make your Terms and Conditions agreement easy to find at any time by displaying it in your site's footer. Make sure users find it at the point of contract creation, such as when they create accounts or complete a purchase.
Get users to agree to it by using the best practice method of an "I Agree" checkbox.

Comprehensive compliance starts with a Privacy Policy.
Comply with the law with our agreements, policies, and consent banners. Everything is included.




